Indexing
A key feature of Qdrant is the effective combination of vector and traditional indexes. It is essential to have this because for vector search to work effectively with filters, having vector index only is not enough. In simpler terms, a vector index speeds up vector search, and payload indexes speed up filtering.
The indexes in the segments exist independently, but the parameters of the indexes themselves are configured for the whole collection.
Not all segments automatically have indexes. Their necessity is determined by the optimizer settings and depends, as a rule, on the number of stored points.
Payload Index
Payload index in Qdrant is similar to the index in conventional document-oriented databases. This index is built for a specific field and type, and is used for quick point requests by the corresponding filtering condition.
The index is also used to accurately estimate the filter cardinality, which helps the query planning choose a search strategy.
Creating an index requires additional computational resources and memory, so choosing fields to be indexed is essential. Qdrant does not make this choice but grants it to the user.
To mark a field as indexable, you can use the following:
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/index
{
"field_name": "name_of_the_field_to_index",
"field_schema": "keyword"
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient
client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333")
client.create_payload_index(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
field_name="name_of_the_field_to_index",
field_schema="keyword",
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.createPayloadIndex("{collection_name}", {
field_name: "name_of_the_field_to_index",
field_schema: "keyword",
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{CreateFieldIndexCollectionBuilder, FieldType};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
client
.create_field_index(CreateFieldIndexCollectionBuilder::new(
"{collection_name}",
"name_of_the_field_to_index",
FieldType::Keyword,
))
.await?;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.PayloadSchemaType;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.createPayloadIndexAsync(
"{collection_name}",
"name_of_the_field_to_index",
PayloadSchemaType.Keyword,
null,
null,
null,
null)
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.CreatePayloadIndexAsync(collectionName: "{collection_name}", fieldName: "name_of_the_field_to_index");
You can use dot notation to specify a nested field for indexing. Similar to specifying nested filters.
Available field types are:
keyword- for keyword payload, affects Match filtering conditions.integer- for integer payload, affects Match and Range filtering conditions.float- for float payload, affects Range filtering conditions.bool- for bool payload, affects Match filtering conditions (available as of v1.4.0).geo- for geo payload, affects Geo Bounding Box and Geo Radius filtering conditions.datetime- for datetime payload, affects Range filtering conditions (available as of v1.8.0).text- a special kind of index, available for keyword / string payloads, affects Full Text search filtering conditions.
Payload index may occupy some additional memory, so it is recommended to only use index for those fields that are used in filtering conditions. If you need to filter by many fields and the memory limits does not allow to index all of them, it is recommended to choose the field that limits the search result the most. As a rule, the more different values a payload value has, the more efficiently the index will be used.
Full-text index
Available as of v0.10.0
Qdrant supports full-text search for string payload. Full-text index allows you to filter points by the presence of a word or a phrase in the payload field.
Full-text index configuration is a bit more complex than other indexes, as you can specify the tokenization parameters. Tokenization is the process of splitting a string into tokens, which are then indexed in the inverted index.
To create a full-text index, you can use the following:
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/index
{
"field_name": "name_of_the_field_to_index",
"field_schema": {
"type": "text",
"tokenizer": "word",
"min_token_len": 2,
"max_token_len": 20,
"lowercase": true
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333")
client.create_payload_index(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
field_name="name_of_the_field_to_index",
field_schema=models.TextIndexParams(
type="text",
tokenizer=models.TokenizerType.WORD,
min_token_len=2,
max_token_len=15,
lowercase=True,
),
)
import { QdrantClient, Schemas } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.createPayloadIndex("{collection_name}", {
field_name: "name_of_the_field_to_index",
field_schema: {
type: "text",
tokenizer: "word",
min_token_len: 2,
max_token_len: 15,
lowercase: true,
},
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
payload_index_params::IndexParams, CreateFieldIndexCollectionBuilder, FieldType,
PayloadIndexParams, TextIndexParams, TokenizerType,
};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
client
.create_field_index(
CreateFieldIndexCollectionBuilder::new(
"{collection_name}",
"name_of_the_field_to_index",
FieldType::Text,
)
.field_index_params(PayloadIndexParams {
index_params: Some(IndexParams::TextIndexParams(TextIndexParams {
tokenizer: TokenizerType::Word as i32,
min_token_len: Some(2),
max_token_len: Some(10),
lowercase: Some(true),
})),
}),
)
.await?;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.PayloadIndexParams;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.PayloadSchemaType;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.TextIndexParams;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.TokenizerType;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.createPayloadIndexAsync(
"{collection_name}",
"name_of_the_field_to_index",
PayloadSchemaType.Text,
PayloadIndexParams.newBuilder()
.setTextIndexParams(
TextIndexParams.newBuilder()
.setTokenizer(TokenizerType.Word)
.setMinTokenLen(2)
.setMaxTokenLen(10)
.setLowercase(true)
.build())
.build(),
null,
null,
null)
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.CreatePayloadIndexAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
fieldName: "name_of_the_field_to_index",
schemaType: PayloadSchemaType.Text,
indexParams: new PayloadIndexParams
{
TextIndexParams = new TextIndexParams
{
Tokenizer = TokenizerType.Word,
MinTokenLen = 2,
MaxTokenLen = 10,
Lowercase = true
}
}
);
Available tokenizers are:
word- splits the string into words, separated by spaces, punctuation marks, and special characters.whitespace- splits the string into words, separated by spaces.prefix- splits the string into words, separated by spaces, punctuation marks, and special characters, and then creates a prefix index for each word. For example:hellowill be indexed ash,he,hel,hell,hello.multilingual- special type of tokenizer based on charabia package. It allows proper tokenization and lemmatization for multiple languages, including those with non-latin alphabets and non-space delimiters. See charabia documentation for full list of supported languages supported normalization options. In the default build configuration, qdrant does not include support for all languages, due to the increasing size of the resulting binary. Chinese, Japanese and Korean languages are not enabled by default, but can be enabled by building qdrant from source with--features multiling-chinese,multiling-japanese,multiling-koreanflags.
See Full Text match for examples of querying with full-text index.
Parameterized index
Available as of v1.8.0
We’ve added a parameterized variant to the integer index, which allows
you to fine-tune indexing and search performance.
Both the regular and parameterized integer indexes use the following flags:
lookup: enables support for direct lookup using Match filters.range: enables support for Range filters.
The regular integer index assumes both lookup and range are true. In
contrast, to configure a parameterized index, you would set only one of these
filters to true:
lookup | range | Result |
|---|---|---|
true | true | Regular integer index |
true | false | Parameterized integer index |
false | true | Parameterized integer index |
false | false | No integer index |
The parameterized index can enhance performance in collections with millions
of points. We encourage you to try it out. If it does not enhance performance
in your use case, you can always restore the regular integer index.
Note: If you set "lookup": true with a range filter, that may lead to
significant performance issues.
For example, the following code sets up a parameterized integer index which supports only range filters:
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/index
{
"field_name": "name_of_the_field_to_index",
"field_schema": {
"type": "integer",
"lookup": false,
"range": true
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333")
client.create_payload_index(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
field_name="name_of_the_field_to_index",
field_schema=models.IntegerIndexParams(
type=models.IntegerIndexType.INTEGER,
lookup=False,
range=True,
),
)
import { QdrantClient, Schemas } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.createPayloadIndex("{collection_name}", {
field_name: "name_of_the_field_to_index",
field_schema: {
type: "integer",
lookup: false,
range: true,
},
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
payload_index_params::IndexParams, CreateFieldIndexCollectionBuilder, FieldType,
IntegerIndexParams, PayloadIndexParams,
};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
client
.create_field_index(
CreateFieldIndexCollectionBuilder::new(
"{collection_name}",
"name_of_the_field_to_index",
FieldType::Integer,
)
.field_index_params(PayloadIndexParams {
index_params: Some(IndexParams::IntegerIndexParams(IntegerIndexParams {
lookup: false,
range: true,
})),
}),
)
.await?;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.IntegerIndexParams;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.PayloadIndexParams;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.PayloadSchemaType;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.createPayloadIndexAsync(
"{collection_name}",
"name_of_the_field_to_index",
PayloadSchemaType.Integer,
PayloadIndexParams.newBuilder()
.setIntegerIndexParams(
IntegerIndexParams.newBuilder().setLookup(false).setRange(true).build())
.build(),
null,
null,
null)
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.CreatePayloadIndexAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
fieldName: "name_of_the_field_to_index",
schemaType: PayloadSchemaType.Integer,
indexParams: new PayloadIndexParams
{
IntegerIndexParams = new()
{
Lookup = false,
Range = true
}
}
);
Vector Index
A vector index is a data structure built on vectors through a specific mathematical model. Through the vector index, we can efficiently query several vectors similar to the target vector.
Qdrant currently only uses HNSW as a dense vector index.
HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World Graph) is a graph-based indexing algorithm. It builds a multi-layer navigation structure for an image according to certain rules. In this structure, the upper layers are more sparse and the distances between nodes are farther. The lower layers are denser and the distances between nodes are closer. The search starts from the uppermost layer, finds the node closest to the target in this layer, and then enters the next layer to begin another search. After multiple iterations, it can quickly approach the target position.
In order to improve performance, HNSW limits the maximum degree of nodes on each layer of the graph to m. In addition, you can use ef_construct (when building index) or ef (when searching targets) to specify a search range.
The corresponding parameters could be configured in the configuration file:
storage:
# Default parameters of HNSW Index. Could be overridden for each collection or named vector individually
hnsw_index:
# Number of edges per node in the index graph.
# Larger the value - more accurate the search, more space required.
m: 16
# Number of neighbours to consider during the index building.
# Larger the value - more accurate the search, more time required to build index.
ef_construct: 100
# Minimal size (in KiloBytes) of vectors for additional payload-based indexing.
# If payload chunk is smaller than `full_scan_threshold_kb` additional indexing won't be used -
# in this case full-scan search should be preferred by query planner and additional indexing is not required.
# Note: 1Kb = 1 vector of size 256
full_scan_threshold: 10000
And so in the process of creating a collection. The ef parameter is configured during the search and by default is equal to ef_construct.
HNSW is chosen for several reasons. First, HNSW is well-compatible with the modification that allows Qdrant to use filters during a search. Second, it is one of the most accurate and fastest algorithms, according to public benchmarks.
Available as of v1.1.1
The HNSW parameters can also be configured on a collection and named vector
level by setting hnsw_config to fine-tune search
performance.
Sparse Vector Index
Available as of v1.7.0
Sparse vectors in Qdrant are indexed with a special data structure, which is optimized for vectors that have a high proportion of zeroes. In some ways, this indexing method is similar to the inverted index, which is used in text search engines.
- A sparse vector index in Qdrant is exact, meaning it does not use any approximation algorithms.
- All sparse vectors added to the collection are immediately indexed in the mutable version of a sparse index.
With Qdrant, you can benefit from a more compact and efficient immutable sparse index, which is constructed during the same optimization process as the dense vector index.
This approach is particularly useful for collections storing both dense and sparse vectors.
To configure a sparse vector index, create a collection with the following parameters:
PUT /collections/{collection_name}
{
"sparse_vectors": {
"text": {
"index": {
"on_disk": false
}
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333")
client.create_collection(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
sparse_vectors={
"text": models.SparseVectorIndexParams(
index=models.SparseVectorIndexType(
on_disk=False,
),
),
},
)
import { QdrantClient, Schemas } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.createCollection("{collection_name}", {
sparse_vectors: {
"splade-model-name": {
index: {
on_disk: false
}
}
}
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
CreateCollectionBuilder, SparseIndexConfigBuilder, SparseVectorParamsBuilder,
SparseVectorsConfigBuilder,
};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
let mut sparse_vectors_config = SparseVectorsConfigBuilder::default();
sparse_vectors_config.add_named_vector_params(
"splade-model-name",
SparseVectorParamsBuilder::default()
.index(SparseIndexConfigBuilder::default().on_disk(true)),
);
client
.create_collection(
CreateCollectionBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.sparse_vectors_config(sparse_vectors_config),
)
.await?;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections;
QdrantClient client = new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.createCollectionAsync(
Collections.CreateCollection.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setSparseVectorsConfig(
Collections.SparseVectorConfig.newBuilder().putMap(
"splade-model-name",
Collections.SparseVectorParams.newBuilder()
.setIndex(
Collections.SparseIndexConfig
.newBuilder()
.setOnDisk(false)
.build()
).build()
).build()
).build()
).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.CreateCollectionAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
sparseVectorsConfig: ("splade-model-name", new SparseVectorParams{
Index = new SparseIndexConfig {
OnDisk = false,
}
})
);
The following parameters may affect performance:
on_disk: true- The index is stored on disk, which lets you save memory. This may slow down search performance.on_disk: false- The index is still persisted on disk, but it is also loaded into memory for faster search.
Unlike a dense vector index, a sparse vector index does not require a pre-defined vector size. It automatically adjusts to the size of the vectors added to the collection.
Note: A sparse vector index only supports dot-product similarity searches. It does not support other distance metrics.
IDF Modifier
Available as of v1.10.0
For many search algorithms, it is important to consider how often an item occurs in a collection. Intuitively speaking, the less frequently an item appears in a collection, the more important it is in a search.
This is also known as the Inverse Document Frequency (IDF). It is used in text search engines to rank search results based on the rarity of a word in a collection.
IDF depends on the currently stored documents and therefore can’t be pre-computed in the sparse vectors in streaming inference mode. In order to support IDF in the sparse vector index, Qdrant provides an option to modify the sparse vector query with the IDF statistics automatically.
The only requirement is to enable the IDF modifier in the collection configuration:
PUT /collections/{collection_name}
{
"sparse_vectors": {
"text": {
"modifier": "idf"
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333")
client.create_collection(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
sparse_vectors={
"text": models.SparseVectorParams(
modifier=models.Modifier.IDF,
),
},
)
import { QdrantClient, Schemas } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.createCollection("{collection_name}", {
sparse_vectors: {
"text": {
modifier: "idf"
}
}
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
CreateCollectionBuilder, Modifier, SparseVectorParamsBuilder, SparseVectorsConfigBuilder,
};
use qdrant_client::{Qdrant, QdrantError};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
let mut sparse_vectors_config = SparseVectorsConfigBuilder::default();
sparse_vectors_config.add_named_vector_params(
"text",
SparseVectorParamsBuilder::default().modifier(Modifier::Idf),
);
client
.create_collection(
CreateCollectionBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.sparse_vectors_config(sparse_vectors_config),
)
.await?;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.CreateCollection;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.Modifier;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.SparseVectorConfig;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Collections.SparseVectorParams;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.createCollectionAsync(
CreateCollection.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setSparseVectorsConfig(
SparseVectorConfig.newBuilder()
.putMap("text", SparseVectorParams.newBuilder().setModifier(Modifier.Idf).build()))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.CreateCollectionAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
sparseVectorsConfig: ("text", new SparseVectorParams {
Modifier = Modifier.Idf,
})
);
Qdrant uses the following formula to calculate the IDF modifier:
$$ \text{IDF}(q_i) = \ln \left(\frac{N - n(q_i) + 0.5}{n(q_i) + 0.5}+1\right) $$
Where:
Nis the total number of documents in the collection.nis the number of documents containing non-zero values for the given vector element.
Filtrable Index
Separately, a payload index and a vector index cannot solve the problem of search using the filter completely.
In the case of weak filters, you can use the HNSW index as it is. In the case of stringent filters, you can use the payload index and complete rescore. However, for cases in the middle, this approach does not work well.
On the one hand, we cannot apply a full scan on too many vectors. On the other hand, the HNSW graph starts to fall apart when using too strict filters.
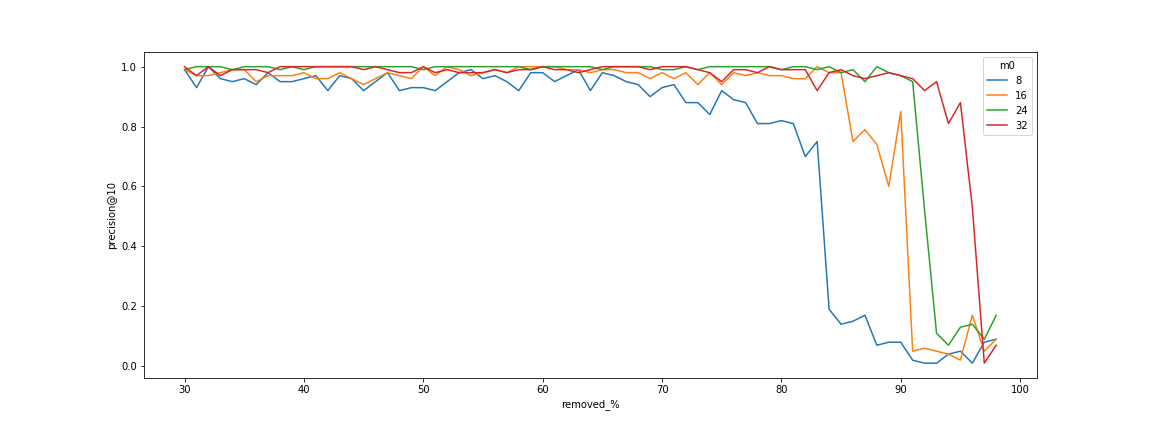

You can find more information on why this happens in our blog post. Qdrant solves this problem by extending the HNSW graph with additional edges based on the stored payload values.
Extra edges allow you to efficiently search for nearby vectors using the HNSW index and apply filters as you search in the graph.
This approach minimizes the overhead on condition checks since you only need to calculate the conditions for a small fraction of the points involved in the search.























