Semantic Cache: Accelerating AI with Lightning-Fast Data Retrieval
Daniel Romero, David Myriel
·May 07, 2024

What is Semantic Cache?
Semantic cache is a method of retrieval optimization, where similar queries instantly retrieve the same appropriate response from a knowledge base.
Semantic cache differs from traditional caching methods. In computing, cache refers to high-speed memory that efficiently stores frequently accessed data. In the context of vector databases, a semantic cache improves AI application performance by storing previously retrieved results along with the conditions under which they were computed. This allows the application to reuse those results when the same or similar conditions occur again, rather than finding them from scratch.
The term “semantic” implies that the cache takes into account the meaning or semantics of the data or computation being cached, rather than just its syntactic representation. This can lead to more efficient caching strategies that exploit the structure or relationships within the data or computation.
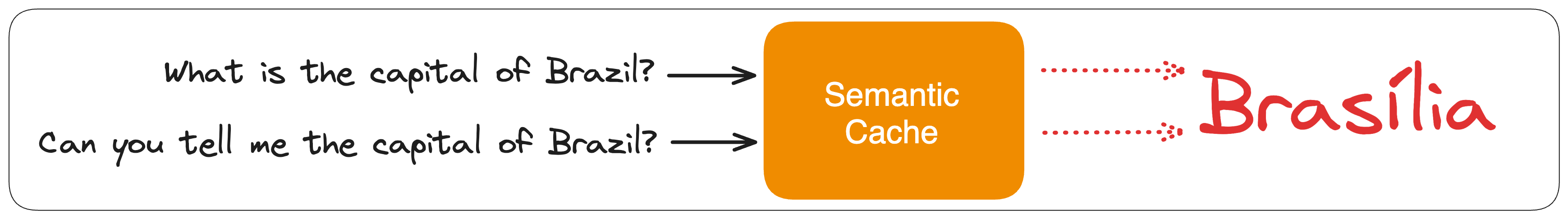
Traditional caches operate on an exact match basis, while semantic caches search for the meaning of the key rather than an exact match. For example, “What is the capital of Brazil?” and “Can you tell me the capital of Brazil?” are semantically equivalent, but not exact matches. A semantic cache recognizes such semantic equivalence and provides the correct result.
In this blog and video, we will walk you through how to use Qdrant to implement a basic semantic cache system. You can also try the notebook example for this implementation.
Semantic Cache in RAG: the Key-Value Mechanism
Semantic cache is increasingly used in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) applications. In RAG, when a user asks a question, we embed it and search our vector database, either by using keyword, semantic, or hybrid search methods. The matched context is then passed to a Language Model (LLM) along with the prompt and user question for response generation.
Qdrant is recommended for setting up semantic cache as semantically evaluates the response. When semantic cache is implemented, we store common questions and their corresponding answers in a key-value cache. This way, when a user asks a question, we can retrieve the response from the cache if it already exists.
Diagram: Semantic cache improves RAG by directly retrieving stored answers to the user. Follow along with the gif and see how semantic cache stores and retrieves answers.

When using a key-value cache, it’s important to consider that slight variations in question wording can lead to different hash values. The two questions convey the same query but differ in wording. A naive cache search might fail due to distinct hashed versions of the questions. Implementing a more nuanced approach is necessary to accommodate phrasing variations and ensure accurate responses.
To address this challenge, a semantic cache can be employed instead of relying solely on exact matches. This entails storing questions, answers, and their embeddings in a key-value structure.
When a user poses a question, a semantic search by Qdrant is conducted across all cached questions to identify the most similar one. If the similarity score surpasses a predefined threshold, the system assumes equivalence between the user’s question and the matched one, providing the corresponding answer accordingly.
Benefits of Semantic Cache for AI Applications
Semantic cache contributes to scalability in AI applications by making it simpler to retrieve common queries from vast datasets. The retrieval process can be computationally intensive and implementing a cache component can reduce the load.
For instance, if hundreds of users repeat the same question, the system can retrieve the precomputed answer from the cache rather than re-executing the entire process. This cache stores questions as keys and their corresponding answers as values, providing an efficient means to handle repeated queries.
There are potential cost savings associated with utilizing semantic cache. Using a semantic cache eliminates the need for repeated searches and generation processes for similar or duplicate questions, thus saving time and LLM API resources, especially when employing costly language model calls like OpenAI’s.
When to Use Semantic Cache?
For applications like question-answering systems where facts are retrieved from documents, caching is beneficial due to the consistent nature of the queries. However, for text generation tasks requiring varied responses, caching may not be ideal as it returns previous responses, potentially limiting variation. Thus, the decision to use caching depends on the specific use case.
Using a cache might not be ideal for applications where diverse responses are desired across multiple queries. However, in question-answering systems, caching is advantageous since variations are insignificant. It serves as an effective performance optimization tool for chatbots by storing frequently accessed data.
One strategy involves creating ad-hoc patches for chatbot dialogues, where commonly asked questions are pre-mapped to prepared responses in the cache. This allows the chatbot to swiftly retrieve and deliver responses without relying on a Language Model (LLM) for each query.
Implement Semantic Cache: A Step-by-Step Guide
The first part of this video explains how caching works. In the second part, you can follow along with the code with our notebook example.
Embrace the Future of AI Data Retrieval
Qdrant offers the most flexible way to implement vector search for your RAG and AI applications. You can test out semantic cache on your free Qdrant Cloud instance today! Simply sign up for or log into your Qdrant Cloud account and follow our documentation.
You can also deploy Qdrant locally and manage via our UI. To do this, check our Hybrid Cloud!



