How Mixpeek Uses Qdrant for Efficient Multimodal Feature Stores
Daniel Azoulai
·April 08, 2025

On this page:
How Mixpeek Uses Qdrant for Efficient Multimodal Feature Stores

About Mixpeek
Mixpeek is a multimodal data processing and retrieval platform designed for developers and data teams. Founded by Ethan Steininger, a former MongoDB search specialist, Mixpeek enables efficient ingestion, feature extraction, and retrieval across diverse media types including video, images, audio, and text.
The Challenge: Optimizing Feature Stores for Complex Retrievers
As Mixpeek’s multimodal data warehouse evolved, their feature stores needed to support increasingly complex retrieval patterns. Initially using MongoDB Atlas’s vector search, they encountered limitations when implementing hybrid retrievers combining dense and sparse vectors with metadata pre-filtering.
A critical limitation emerged when implementing late interaction techniques like ColBERT across video embeddings, which requires multi-vector indexing. MongoDB’s kNN search could not support these multi-vector representations for this contextual understanding.
Another one of Mixpeek’s customers required reverse video search for programmatic ad-serving, where retrievers needed to identify high-converting video segments across massive object collections - a task that proved inefficient with MongoDB’s general-purpose database feature stores.
“We eliminated hundreds of lines of code with what was previously a MongoDB kNN Hybrid search when we replaced it with Qdrant as our feature store.” — Ethan Steininger, Mixpeek Founder
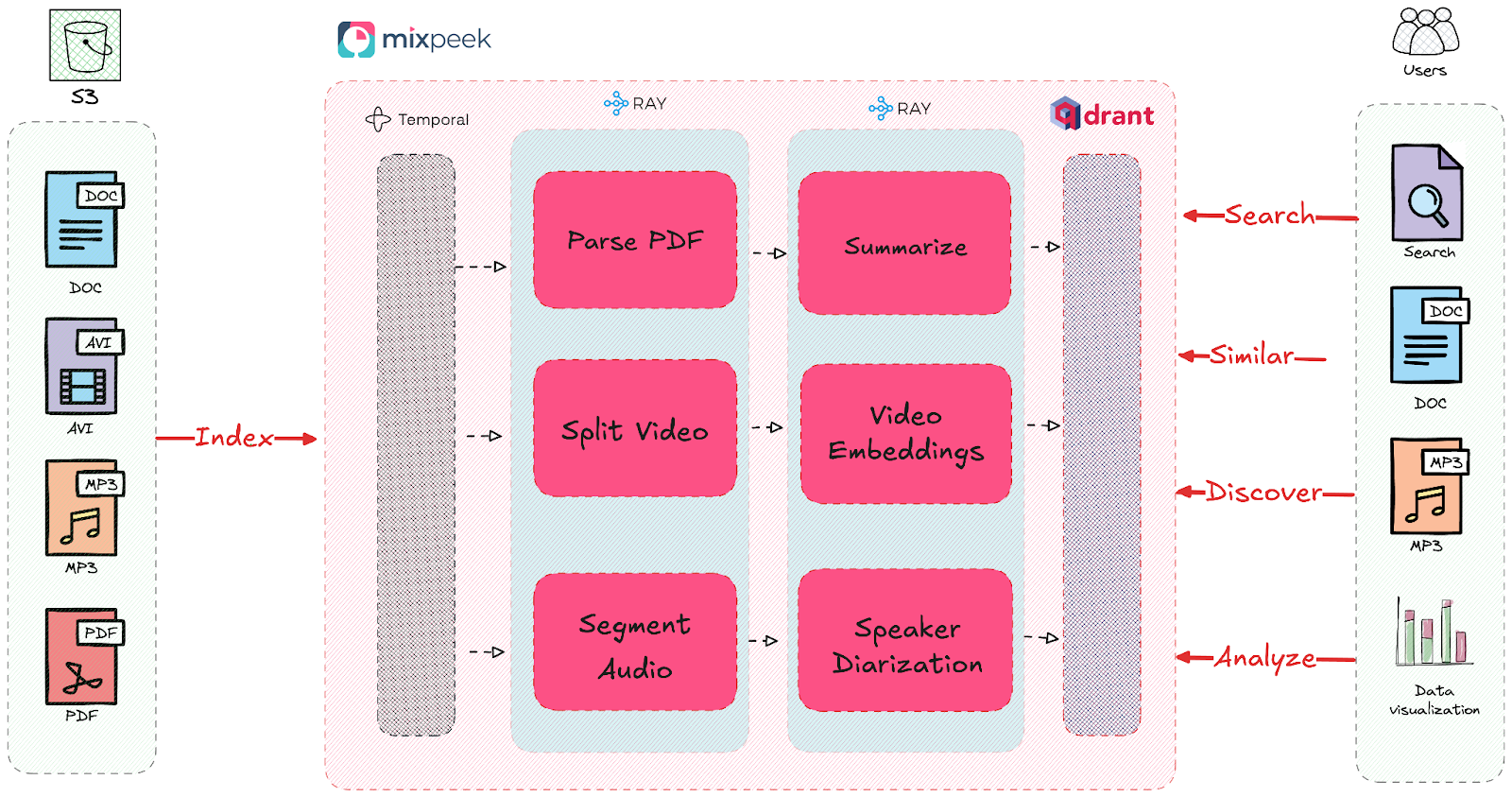
Why Mixpeek Chose Qdrant for Feature Stores
After evaluating multiple options including Postgres with pgvector and MongoDB’s kNN search, Mixpeek selected Qdrant to power their feature stores due to its specialization in vector search and integration capabilities with their retrieval pipelines. Qdrant’s native support for multi-vector indexing was crucial for implementing late interaction techniques like ColBERT, which MongoDB couldn’t efficiently support.
Simplifying Hybrid Retrievers
Previously, Mixpeek maintained complex custom logic to merge results from different feature stores. Qdrant’s native support for Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) streamlined their retriever implementations, reducing hybrid search code by 80%. The multi-vector capabilities also enabled more sophisticated retrieval methods that better captured semantic relationships.
“Hybrid retrievers with our previous feature stores were challenging. With Qdrant, it just worked.”
40% Faster Query Times with Parallel Retrieval
For collections with billions of features, Qdrant’s prefetching capabilities enabled parallel retrieval across multiple feature stores. This cut retriever query times by 40%, dropping from ~2.5s to 1.3-1.6s.
“Prefetching in Qdrant lets us execute multiple feature store retrievals simultaneously and then combine the results, perfectly supporting our retriever pipeline architecture.”
Optimizing SageMaker Feature Extraction Workflows
Mixpeek uses Amazon SageMaker for feature extraction, and database queries were a significant bottleneck. By implementing Qdrant as their feature store, they reduced query overhead by 50%, streamlining their ingestion pipelines.
“We were running inference with SageMaker for feature extraction, and our feature store queries used to be a significant bottleneck. Qdrant shaved off a lot of that time.”
Supporting Mixpeek’s Taxonomy and Clustering Architecture
Qdrant proved particularly effective for implementing Mixpeek’s taxonomy and clustering capabilities:
Taxonomies (JOIN Analogue)
Qdrant’s payload filtering facilitated efficient implementation of both flat and hierarchical taxonomies, enabling document enrichment through similarity-based “joins” across collections.
Clustering (GROUP BY Analogue)
The platform’s batch vector search capabilities streamlined document clustering based on feature similarity, providing an effective implementation of the traditional “group by” interface.
Measurable Improvements After Feature Store Migration
The migration to Qdrant as Mixpeek’s feature store brought significant improvements:
- 40% Faster Retrievers: Reduced query times from ~2.5s to 1.3-1.6s
- 80% Code Reduction: Simplified retriever implementations
- Improved Developer Productivity: Easier implementation of complex retrieval patterns
- Optimized Scalability: Better performance at billion-feature scale
- Enhanced Multimodal Retrieval: Better support for combining different feature types
Future Direction: Supporting Diverse Multimodal Use Cases
Mixpeek’s architecture excels by pre-building specialized feature extractors tightly coupled with retriever pipelines, enabling efficient processing across diverse multimodal use cases.
This architectural approach ensures that features extracted during ingestion are precisely what retrievers need for efficient querying, eliminating translation layers that typically slow down multimodal systems.
“We’re moving towards sophisticated multimodal ontologies, and Qdrant’s specialized capabilities as a feature store will be essential for these advanced retriever strategies.”
Conclusion: Specialized Feature Stores for Multimodal Data Warehousing
Mixpeek’s journey highlights the importance of specialized feature stores in a multimodal data warehouse architecture. Qdrant’s focus on vector search efficiency made it the ideal choice for powering Mixpeek’s feature stores, enabling more efficient retrievers and ingestion pipelines.


























