Optimizing ColPali for Retrieval at Scale, 13x Faster Results
Evgeniya Sukhodolskaya, Sabrina Aquino
·November 27, 2024

On this page:
ColPali is a fascinating leap in document retrieval. Its precision in handling visually rich PDFs is phenomenal, but scaling it to handle real-world datasets comes with its share of computational challenges.
Here’s how we solved these challenges to make ColPali 13x faster without sacrificing the precision it’s known for.
The Scaling Dilemma
ColPali generates 1,030 vectors for just one page of a PDF. While this is manageable for small-scale tasks, in a real-world production setting where you may need to store hundreds od thousands of PDFs, the challenge of scaling becomes significant.
Consider this scenario:
- Dataset Size: 20,000 PDF pages.
- Number of Vectors: Each page generates ~1,000 vectors of 128 dimensions.
The total number of comparisons is calculated as:
That’s trillions of comparisons needed to build the index. Even advanced indexing algorithms like HNSW struggle with this scale, as computational costs grow quadratically with amount of multivectors per page.
We turned to a hybrid optimization strategy combining pooling (to reduce computational overhead) and reranking (to preserve accuracy).
Before we go any deeper, watch our Webinar video for the full demo walkthrough.
For those eager to explore, the codebase is available here.
Two-Stage Retrieval Process
Pooling
Pooling is well-known in machine learning as a way to compress data while keeping important information. For ColPali, we reduced 1,030 vectors per page to just 38 vectors by pooling rows in the document’s 32x32 grid.
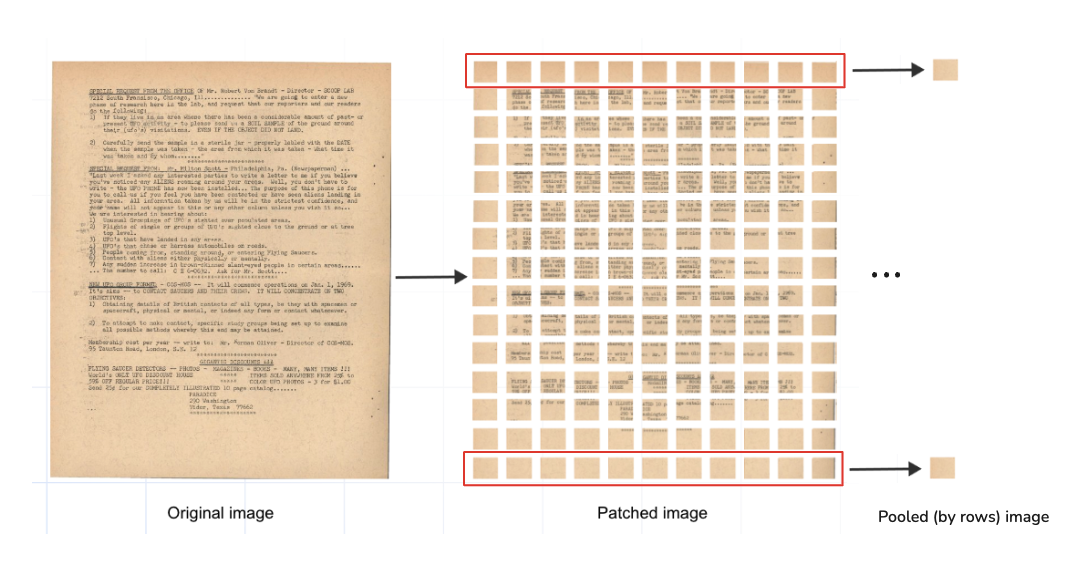
Max and mean pooling are the two most popular types, so we decided to test both approaches on the rows of the grid. Likewise, we could apply pooling on columns, which we plan to explore in the future.
- Mean Pooling: Averages values across rows.
- Max Pooling: Selects the maximum value for each feature.
32 vectors represent the pooled rows, while 6 vectors encode contextual information derived from ColPali’s special tokens (e.g.,
For our experiments, we chose to preserve these 6 additional vectors.
The “ColPali as a Reranker” Experiment
Pooling drastically reduces retrieval costs, but there’s a risk of losing fine-grained precision. To address this, we implemented a two-stage retrieval system, where embeddings generated with ColPali were max/mean pooled by grid rows to create lightweight vectors for the initial retrieval stage, followed by reranking with the original high-resolution embeddings:
- Pooled Retrieval: Quickly retrieves the top 200 candidates using lightweight pooled embeddings.
- Full Reranking: Refines these candidates using the original, high-resolution embeddings, delivering the final top 20 results.
Implementation
We created a custom dataset with over 20,000 unique PDF pages by merging:
- ViDoRe Benchmark: Designed for PDF documents retrieval evaluation.
- UFO Dataset: Visually rich documents paired with synthetic queries generated by Daniel van Strien.
- DocVQA Dataset: A large set of document-derived Q&A pairs.
Each document was processed into 32x32 grids, generating both full-resolution and pooled embeddings. Full-resolution embeddings consisted of 1,030 vectors per page, while pooled embeddings included mean and max pooling variants.
All embeddings were were stored and kept in RAM to avoid caching effects during retrieval speed experiments.
Experiment Setup
We evaluated retrieval quality with 1,000 queries. First, pooled embeddings retrieved the top 200 candidates. Then, full-resolution embeddings reranked them to produce the final top 20 results.
To measure performance, we used:
- NDCG@20: Measures ranking quality (how well the top results align with expectations).
- Recall@20: Measures the overlap between this method and the original ColPali retrieval.
Results
The experiment showed promising improvements in speed and accuracy. Retrieval time improved 13x compared to using full-resolution embeddings alone.
Metrics
| Pooling Type | NDCG@20 | Recall@20 |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 0.952 | 0.917 |
| Max | 0.759 | 0.656 |
Mean pooling preserved nearly identical quality to the original ColPali, with NDCG@20 = 0.952 and Recall@20 = 0.917. Max pooling did not perform well enough to be considered viable since it sacrificed significant accuracy without delivering a meaningful speed advantage.
What’s Next?
Future experiments could push these results even further:
- Investigating column-wise pooling for additional compression.
- Testing half-precision (float16) vectors to balance memory use and speed.
- Skipping special multivectors during prefetch to streamline retrieval.
- Combining quantization with oversampling for even faster search.
Try It Yourself
Curious to see this in action? Explore the full codebase and experiment with ColPali optimizations:
- Demo Notebook: GitHub Repository
- Webinar Walkthrough: Watch Here
Join the community and share your results!



































