Qdrant Edge: Vector Search for Embedded AI
Qdrant
·July 29, 2025
On this page:
Qdrant Edge (Private Beta): Vector Search for Embedded AI
Over the past two years, vector search has become foundational infrastructure for AI applications, from retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to agentic reasoning. But as AI systems extend beyond cloud-hosted inference into the physical world - running on devices like robots, kiosks, home assistants, and mobile phones - new constraints emerge. Low-latency retrieval, multimodal inputs, and bandwidth-independent operation will become first-class requirements. Qdrant Edge is our response to this shift.
From Static RAG to Embedded AI: Three Waves of Vector Search
Vector databases first gained widespread adoption during the rise of RAG 1.0, where they served as context providers for LLMs performing text-based tasks such as document search and chatbot Q&A. In these applications, performance was defined by filtering speed, recall accuracy, and support for hybrid search over structured metadata.
This evolved into the Agentic AI wave, where vector search engines are becoming long-term memory modules within autonomous (software) agents. Requirements expanded to include low-latency updates, token-level reranking, and multimodal retrieval. Qdrant is powering thousands of these applications in production today - supporting with real-time search, advanced metadata filters, and native multivector semantics for ColBERT-style workflows.
Now, a third wave is emerging: Embedded AI. This wave brings vector-based reasoning to environments without reliable network access or cloud compute. Here, the vector database must operate on-device, under tight constraints of memory, power, and I/O. Traditional vector stores - designed for large server environments - are not suitable.
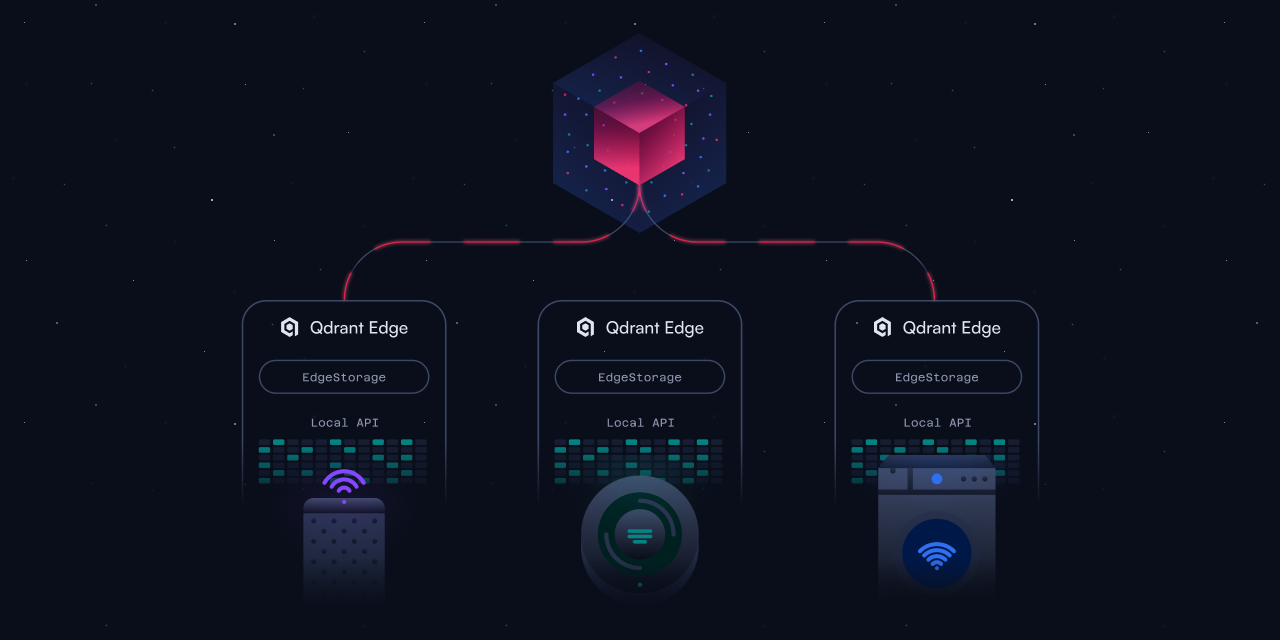
Qdrant Edge: Built for On-Device Vector Search
Qdrant Edge is a lightweight, embedded vector search engine designed to run on local hardware with limited persistent background threads, network access, or centralized coordination. It retains Qdrant’s core search and filtering capabilities but is re-architected to operate as a minimal, local library that integrates directly into AI workflows on edge devices.
Key capabilities include:
In-process execution: Qdrant Edge runs as a library, not a service. There are no background optimizers or update threads. All operations - including search and indexing - are synchronous and under the control of the application.
Minimal footprint: Designed for memory- and compute-constrained environments.
Multitenancy-aware: Suitable for deployments where each device (e.g., a robot or mobile unit) functions as a tenant with isolated data and compute.
Use Cases and Design Targets
Qdrant Edge is built for scenarios where inference and decision-making happen at the edge, close to the data. Example environments include:
- Robotics and autonomous navigation: Real-time perception and decision-making with multimodal vector inputs (e.g., camera, LiDAR, radar).
- Mobile devices: Local assistant functionality with offline access, on-device personalization, and privacy-preserving search.
- Point-of-sale systems: Product similarity, anomaly detection, and decision support in disconnected or bandwidth-constrained environments.
- IoT agents: Local retrieval for condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, or sensor fusion.
In each of these domains, the system demands are orthogonal to those of cloud-hosted vector infrastructure: short-lived processes, strict latency bounds, and minimal runtime dependencies.
Why Qdrant Works Well on the Edge
Qdrant is the first production-grade vector database actively developing for the embedded systems domain. Qdrant Edge is a dedicated engineering effort to build a performant, extensible, embeddable vector engine for ML practitioners working at the edge, based on the original lightweight design of Qdrant and builds on the architectural strengths that Qdrant has been recognized for:
- Custom, filterable HNSW implementation
- Hybrid search across sparse and dense modalities
- Multivector compatibility and multimodal indexing
- Real-time ingestion
Qdrant Edge carries these capabilities forward into a new class of deployment environments.
Apply for the Private Research Beta
Qdrant Edge is currently in private beta. Due to the highly targeted nature of this release, we will be selecting a limited number of partners who are actively building AI systems for embedded or real-time environments.
If you’re working on robotics, edge inference, autonomous systems, or device-native assistants, we encourage you to apply.
Apply to Join the Qdrant Edge Beta
Closing Thoughts
Embedded AI systems bring unique constraints that require rethinking how we design infrastructure like vector databases. Qdrant Edge represents a new class of tooling - one that treats on-device reasoning as a first-class capability. We’re excited to collaborate with forward-thinking teams building the next generation of intelligent systems.
FAQs
Who is Qdrant Edge for?
Teams building AI systems that need fast, local vector search on embedded or resource-constrained devices, such as robots, mobile apps, or IoT hardware.
Is this available to all Qdrant users?
Not yet. Qdrant Edge is in private beta. We’re selecting a limited number of partners based on technical fit and active edge deployment scenarios.
What are the minimum requirements to join the beta?
You should have a clear use case for on-device or offline vector search. Preference is given to companies working with embedded hardware or deploying agents at the edge.
How do I get access?
Qdrant Edge is currently in private beta. If you’re building edge-native or embedded AI systems and want early access, apply to join the beta.
































