Qdrant for Research: The Story Behind ETH & Stanford’s MIRIAD Dataset
Evgeniya Sukhodolskaya & Daniel Azoulai
·July 23, 2025

On this page:
This summer, researchers from ETH Zurich and Stanford released MIRIAD, an open source dataset of 5.8 million medical Question Answer pairs, each grounded in peer-reviewed literature.
A dataset of this scale has the potential to become an ultimate solution to the lack of structured, rich-in-context, high-quality data in the medical field. It is a powerful measure for a significant reduction of hallucinations in medical AI applications, created to be a knowledge base for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and a source for downstreaming embedding models.
One of the proudest moments for us was a realization that Qdrant was a part of MIRIAD’s story, powering its storage and RAG experiments.
We spoke to two lead authors of MIRIAD, Qinyue Zheng (ETH) and Salman Abdullah (Stanford), to learn the motivation behind MIRIAD, how its authors see its future, and why Qdrant was a deliberate choice for the research team.
Why Medical AI Needed MIRIAD
Large Language Models’ hallucinations, already problematic in general domains, are a matter of life or death in the medical field. Hence, to mitigate these risks and make medical AI applications usable, the most promising way seems to be augmenting LLMs with structured, grounded knowledge.
Many modern RAG and agentic systems, including those used in medical AI, often rely on raw, unstructured data that is noisy and poorly aligned with downstreaming tasks. It was clear that the intersection of medicine and AI could benefit significantly from a dataset with long-form, rich-in-context Q&A pairs.
All existing datasets in the field like MedQA-USMLE or PubMedQA were either limited to multiple-choice QA formats or focused on a narrow selection of medical paper sections like abstracts or conclusions, leaving alarming knowledge gaps.
The goal of MIRIAD’s authors was to create a large-scale dataset that is:
- Structured & information-dense;
- Comprehensive, covering diverse niches in medicine with sufficient depth;
- Grounded & trustworthy, so each piece of information can be traced back to a peer-reviewed paper.
And organize medical knowledge in a way that could support clinicians and engineers in medical AI alike.
How MIRIAD Was Created
MIRIAD was built on top of the Semantic Scholar Open Research Corpus (S2ORC), currently leveraging a curated subset of 900,000 medical papers, with plans to expand a broader coverage as the dataset evolves.
Question Answer pairs in the dataset were generated from fixed-size chunks using GPT-3.5-Turbo, followed by a multi-stage filtering pipeline ensuring the quality of the resulting dataset in three stages:
- Automated filtering with regular expressions;
- Filtering with classifier based on a Mistral-7B model, trained on GPT-4-flagged low-quality examples;
- Human-in-the-loop expert labeling, which showed strong agreement between medical experts and GPT-4: 92.3% on groundedness, 88.6% on factuality, and 78.4% on relevance.
The full outline of the pipeline behind MIRIAD is visually summarized here:
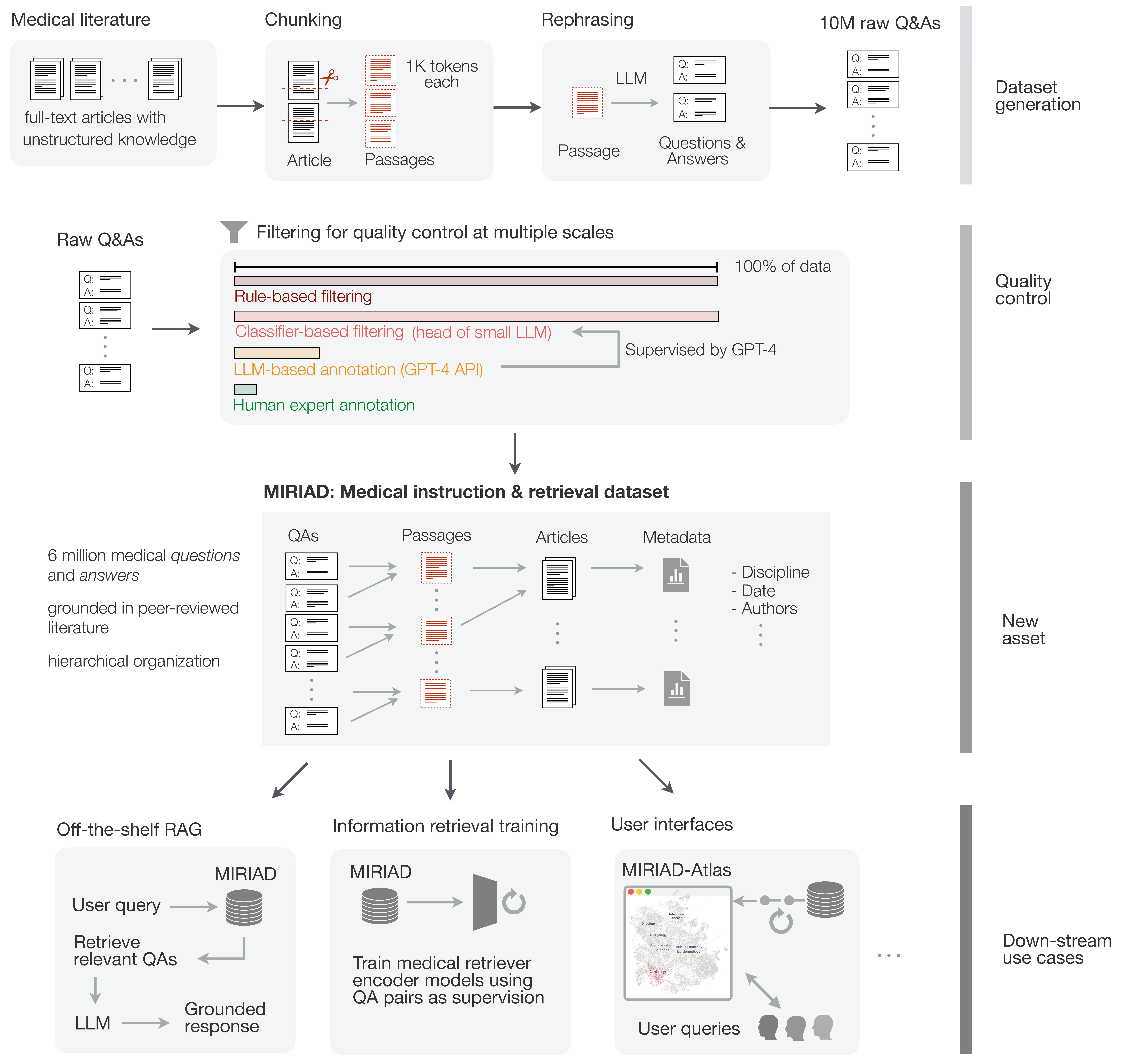
Overview of the data generation pipeline of MIRIAD
Source: “MIRIAD: Augmenting LLMs with millions of medical query-response pairs.”
Qdrant’s Role in MIRIAD
Qdrant was a deliberate choice to handle retrieval of millions of Q&A pairs under the hood of MIRIAD’s RAG experiments. The deciding factors were the simplicity of use and readability of our documentation, speed and scalability, and, what is especially valuable for researchers, Qdrant being open source.
“For us, we had millions of data points to deal with and somehow the retrieval was super fast with Qdrant!” - Qinyue Zheng
These capabilities allowed researchers to focus on experiments instead of struggles of the infrastructure setup.
Results
The results of various benchmarks clearly show that structured, high-quality datasets can significantly improve the reliability of LLMs in high stakes domains.
Augmenting MIRIAD improved:
- Accuracy on medical QA benchmarks by up to 6.7% compared to unstructured RAG baselines, with the same source corpus and retrieval budget;
- LLMs’ medical hallucination detection capabilities by 22 - 37 percentage points.
The final MIRIAD dataset contains 5,821,948 Question Answer pairs, each linked to a source passage and paper, spanning 56 medical topics.
It is open sourced on HuggingFace, along with source code and a detailed guide for full gathering and benchmarking replication, including embeddings generation and indexing to Qdrant, and RAG setup.
Additionally, to make the dataset accessible not only to engineers in medical AI but also to clinicians, authors of MIRIAD developed MIRIAD Atlas, an interactive map of UMAP-based dimensionality-reduced embeddings (similar to how one can visualize and study datasets in Qdrant’s WebUI).
Looking Ahead
The researchers’ goal is to maintain and expand MIRIAD, keeping it current with new medical knowledge on a yearly basis. There are also plans to migrate MIRIAD Atlas to Qdrant, to serve dataset at its full scale, and add support for the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
Yet mainly, MIRIAD aims to inspire researchers, clinicians, and engineers to build more reliable and domain-specific medical AI systems.
“Sky is the limit” - Qinyue Zheng
Authors envision applications such as medical QA agents, medical discipline explorers using the specialty labels in MIRIAD to route among different disciplines, or explainability tools supporting RAG-based applications.
Qdrant in Research
We are happy to see Qdrant helping researchers at the frontier of medical AI come up with achievements that others can build upon!
By reducing engineering overhead, we want researchers to focus on advancing their domain contributions. Apart from handling scale, we see other exciting applications of Qdrant in research. For example, Qdrant could serve as a tool for:
- Deduplication in large-scale datasets based on semantic similarity;
- Diversity sampling for comprehensive training datasets.
As MIRIAD’s authors told us, “the sky is the limit”.
We’re looking forward to seeing Qdrant more and more as a helping hand in further research advancements!
































