Best Practices in RAG Evaluation: A Comprehensive Guide
David Myriel
·November 24, 2024

On this page:
Introduction
This guide will teach you how to evaluate a RAG system for both accuracy and quality. You will learn to maintain RAG performance by testing for search precision, recall, contextual relevance, and response accuracy.
Building a RAG application is just the beginning; it is crucial to test its usefulness for the end-user and calibrate its components for long-term stability.
RAG systems can encounter errors at any of the three crucial stages: retrieving relevant information, augmenting that information, and generating the final response. By systematically assessing and fine-tuning each component, you will be able to maintain a reliable and contextually relevant GenAI application that meets user needs.
Why evaluate your RAG application?
To avoid hallucinations and wrong answers

In the generation phase, hallucination is a notable issue where the LLM overlooks the context and fabricates information. This can lead to responses that are not grounded in reality.
Additionally, the generation of biased answers is a concern, as responses produced by the LLM can sometimes be harmful, inappropriate, or carry an inappropriate tone, thus posing risks in various applications and interactions.
To enrich context augmented to your LLM
Augmentation processes face challenges such as outdated information, where responses may include data that is no longer current. Another issue is the presence of contextual gaps, where there is a lack of relational context between the retrieved documents.
These gaps can result in incomplete or fragmented information being presented, reducing the overall coherence and relevance of the augmented responses.
To maximize the search & retrieval process
When it comes to retrieval, one significant issue with search is the lack of precision, where not all documents retrieved are relevant to the query. This problem is compounded by poor recall, meaning not all relevant documents are successfully retrieved.
Additionally, the “Lost in the Middle” problem indicates that some LLMs may struggle with long contexts, particularly when crucial information is positioned in the middle of the document, leading to incomplete or less useful results.
Recommended frameworks

To simplify the evaluation process, several powerful frameworks are available. Below we will explore three popular ones: Ragas, Quotient AI, and Arize Phoenix.
Ragas: Testing RAG with questions and answers
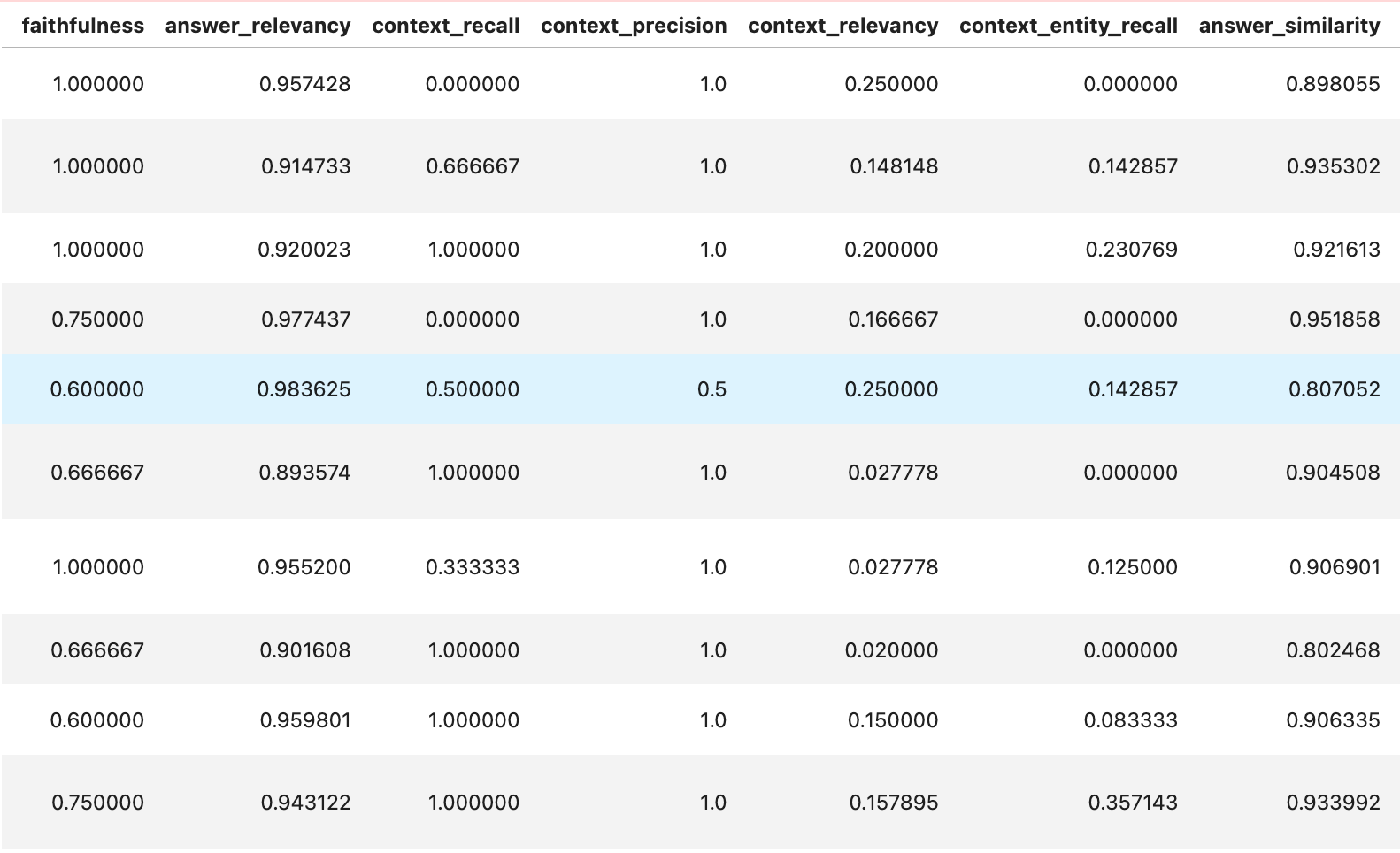
Ragas (or RAG Assessment) uses a dataset of questions, ideal answers, and relevant context to compare a RAG system’s generated answers with the ground truth. It provides metrics like faithfulness, relevance, and semantic similarity to assess retrieval and answer quality.
Figure 1: Output of the Ragas framework, showcasing metrics like faithfulness, answer relevancy, context recall, precision, relevancy, entity recall, and answer similarity. These are used to evaluate the quality of RAG system responses.
Quotient: evaluating RAG pipelines with custom datasets
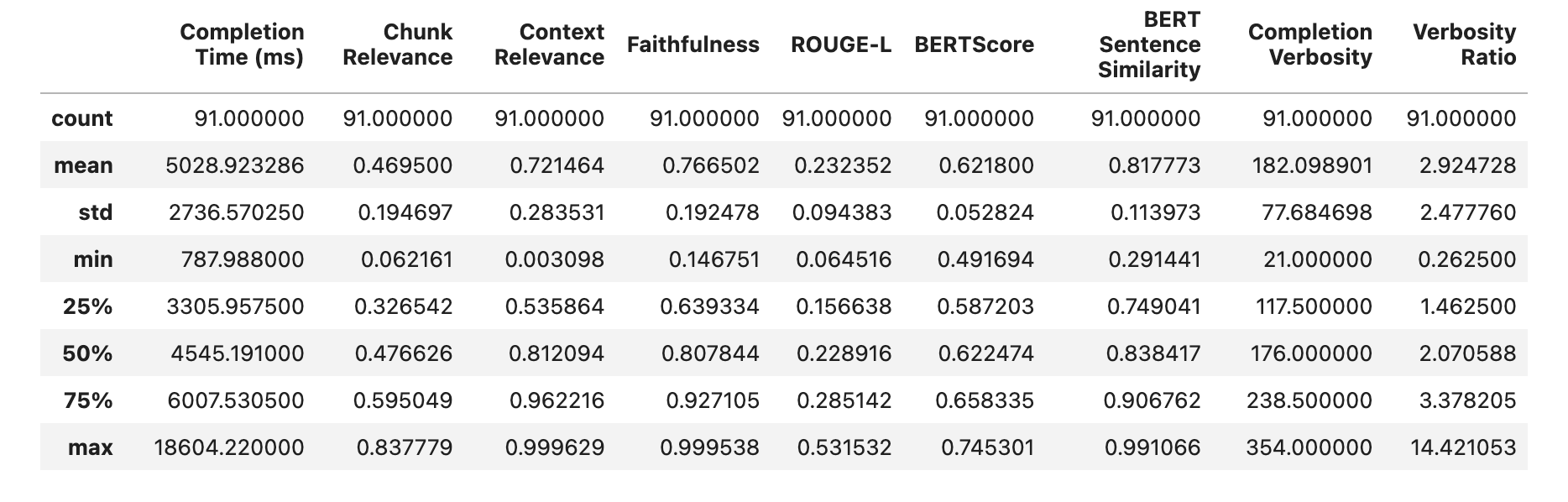
Quotient AI is another platform designed to streamline the evaluation of RAG systems. Developers can upload evaluation datasets as benchmarks to test different prompts and LLMs. These tests run as asynchronous jobs: Quotient AI automatically runs the RAG pipeline, generates responses and provides detailed metrics on faithfulness, relevance, and semantic similarity. The platform’s full capabilities are accessible via a Python SDK, enabling you to access, analyze, and visualize your Quotient evaluation results to discover areas for improvement.
Figure 2: Output of the Quotient framework, with statistics that define whether the dataset is properly manipulated throughout all stages of the RAG pipeline: indexing, chunking, search and context relevance.
Arize Phoenix: Visually Deconstructing Response Generation
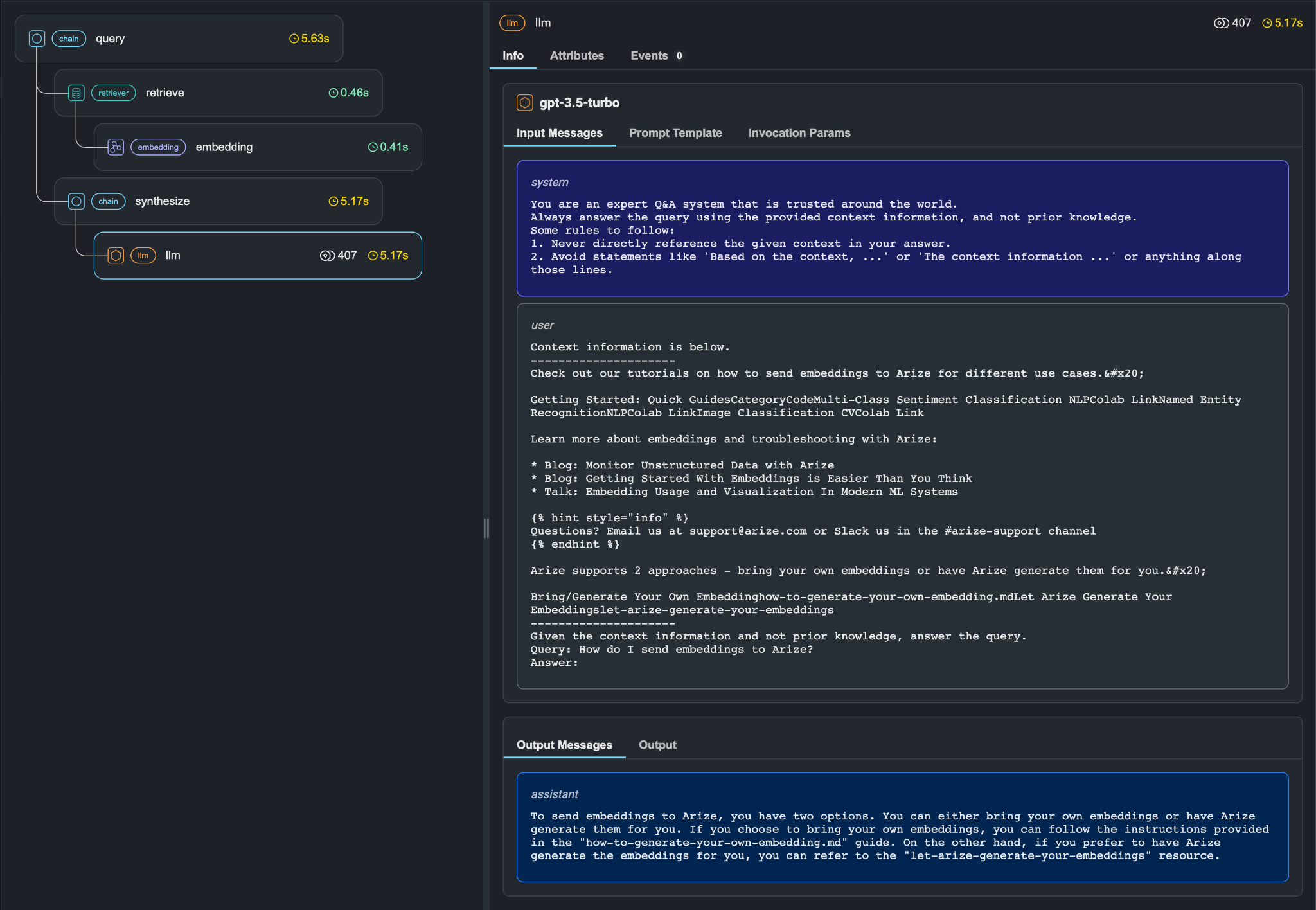
Arize Phoenix is an open-source tool that helps improve the performance of RAG systems by tracking how a response is built step-by-step. You can see these steps visually in Phoenix, which helps identify slowdowns and errors. You can define “evaluators” that use LLMs to assess the quality of outputs, detect hallucinations, and check answer accuracy. Phoenix also calculates key metrics like latency, token usage, and errors, giving you an idea of how efficiently your RAG system is working.
Figure 3: The Arize Phoenix tool is intuitive to use and shows the entire process architecture as well as the steps that take place inside of retrieval, context and generation.
Why your RAG system might be underperforming

You improperly ingested data to the vector database
Improper data ingestion can cause the loss of important contextual information, which is critical for generating accurate and coherent responses. Also, inconsistent data ingestion can cause the system to produce unreliable and inconsistent responses, undermining user trust and satisfaction.
Vector databases support different indexing techniques. In order to know if you are ingesting data properly, you should always check how changes in variables related to indexing techniques affect data ingestion.
Solution: Pay attention to how your data is chunked
Calibrate document chunk size: The chunk size determines data granularity and impacts precision, recall, and relevance. It should be aligned with the token limit of the embedding model.
Ensure proper chunk overlap: This helps retain context by sharing data points across chunks. It should be managed with strategies like deduplication and content normalization.
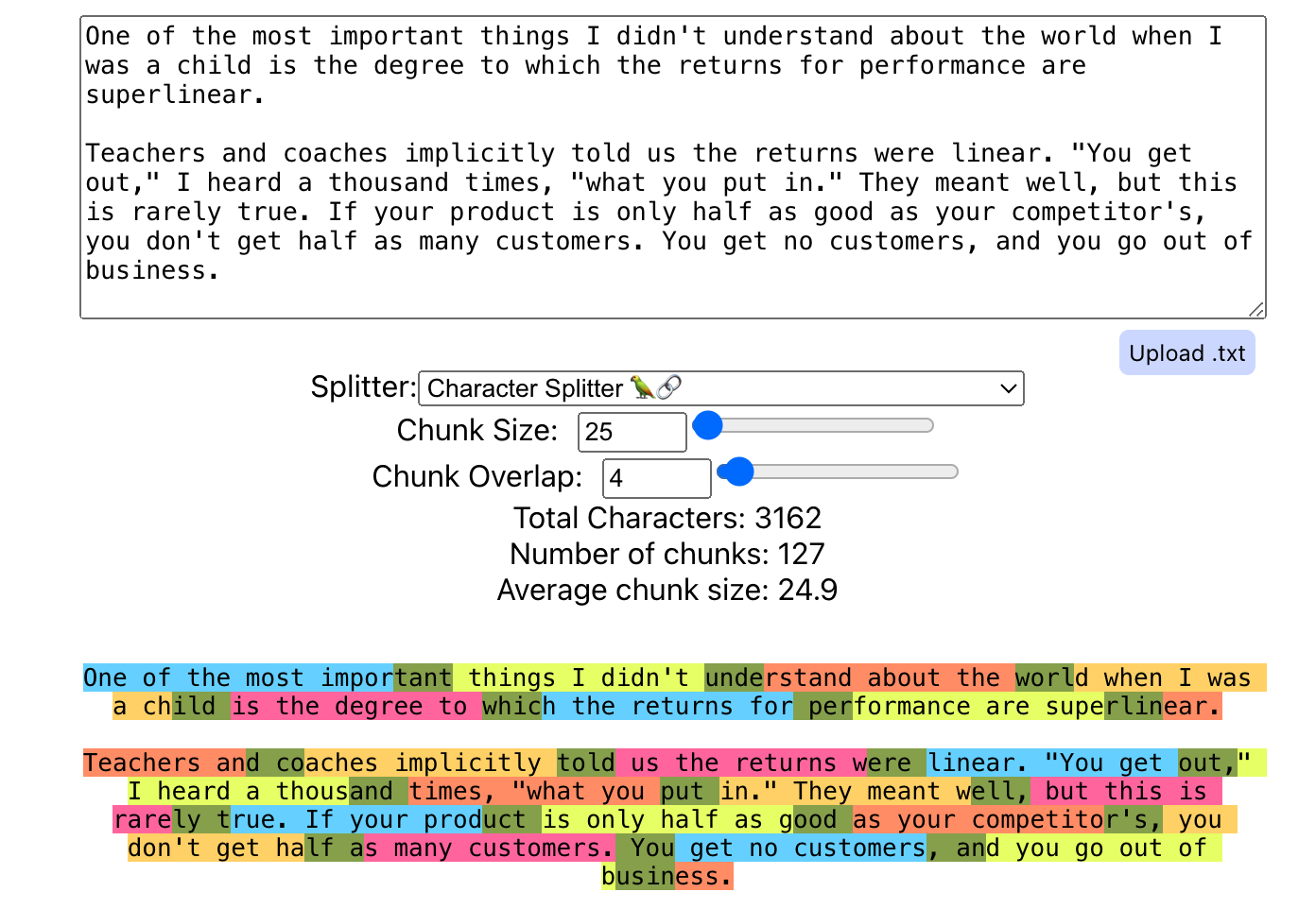
Develop a proper chunking/text splitting strategy: Make sure your chunking/text splitting strategy is tailored to your on data type (e.g., HTML, markdown, code, PDF) and use-case nuances. For example, legal documents may be split by headings and subsections, and medical literature by sentence boundaries or key concepts.
Figure 4: You can use utilities like ChunkViz to visualize different chunk splitting strategies, chunk sizes, and chunk overlaps.
You might be embedding data incorrectly
You want to ensure that the embedding model accurately understands and represents the data. If the generated embeddings are accurate, similar data points will be closely positioned in the vector space. The quality of an embedding model is typically measured using benchmarks like the Massive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB), where the model’s output is compared against a ground-truth dataset.
Solution: Pick the right embedding model
The embedding model plays a critical role in capturing semantic relationships in data.
There are several embedding models you can choose from, and the Massive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB) Leaderboard is a great resource for reference. Lightweight libraries like FastEmbed support the generation of vector embeddings using popular text embedding models.
When choosing an embedding model, retrieval performance and domain specificity. You need to ensure that the model can capture semantic nuances, which affects the retrieval performance. For specialized domains, you may need to select or train a custom embedding model.
Your retrieval procedure isn’t optimized

Semantic retrieval evaluation tests the effectiveness of your data retrieval. There are several metrics you can choose from:
- Precision@k: Measures the number of relevant documents in the top-k search results.
- Mean reciprocal rank (MRR): Considers the position of the first relevant document in the search results.
- Discounted cumulative gain (DCG) and normalized DCG (NDCG): Based on the relevance score of the documents.
By evaluating the retrieval quality using these metrics, you can assess the effectiveness of your retrieval step. For evaluating the ANN algorithm specifically, Precision@k is the most appropriate metric, as it directly measures how well the algorithm approximates exact search results.
Solution: Choose the best retrieval algorithm
Each new LLM with a larger context window claims to render RAG obsolete. However, studies like “Lost in the Middle” demonstrate that feeding entire documents to LLMs can diminish their ability to answer questions effectively. Therefore, the retrieval algorithm is crucial for fetching the most relevant data in the RAG system.
Configure dense vector retrieval: You need to choose the right similarity metric to get the best retrieval quality. Metrics used in dense vector retrieval include Cosine Similarity, Dot Product, Euclidean Distance, and Manhattan Distance.
Use sparse vectors & hybrid search where needed: For sparse vectors, the algorithm choice of BM-25, SPLADE, or BM-42 will affect retrieval quality. Hybrid Search combines dense vector retrieval with sparse vector-based search.
Leverage simple filtering: This approach combines dense vector search with attribute filtering to narrow down the search results.
Set correct hyperparameters: Your Chunking Strategy, Chunk Size, Overlap, and Retrieval Window Size significantly impact the retrieval step and must be tailored to specific requirements.
Introduce re-ranking: Such methods may use cross-encoder models to re-score the results returned by vector search. Re-ranking can significantly improve retrieval and thus RAG system performance.
LLM generation performance is suboptimal
The LLM is responsible for generating responses based on the retrieved context. The choice of LLM ranges from OpenAI’s GPT models to open-weight models. The LLM you choose will significantly influence the performance of a RAG system. Here are some areas to watch out for:
- Response quality: The LLM selection will influence the fluency, coherence, and factual accuracy of generated responses.
- System performance: Inference speeds vary between LLMs. Slower inference speeds can impact response times.
- Domain knowledge: For domain-specific RAG applications, you may need LLMs trained on that domain. Some LLMs are easier to fine-tune than others.
Solution: Test and Critically Analyze LLM Quality
The Open LLM Leaderboard can help guide your LLM selection. On this leaderboard, LLMs are ranked based on their scores on various benchmarks, such as IFEval, GPQA, MMLU-PRO, and others.
Evaluating LLMs involves several key metrics and methods. You can use these metrics or frameworks to evaluate if the LLM is delivering high-quality, relevant, and reliable responses.
Table 1: Methods for Measuring LLM Response Quality
| Column header | Column header |
|---|---|
| Perplexity | Measure how well the model predicts text. |
| Human Evaluation | Rate responses based on relevance, coherence and quality. |
| BLEU | Used in translation tasks to compare generated output with reference translations. Higher scores (0-1) indicate better performance. |
| ROUGE | Evaluates summary quality by comparing generated summaries with reference summaries, calculating precision, recall and F1-score. |
| EleutherAI | A framework to test LLMs on different evaluation tasks. |
| HELM | A framework to evaluate LLMs, focusing on 12 different aspects that are important in real-world model deployments. |
| Diversity | Assesses the variety and uniqueness of responses, with higher scores indicating more diverse outputs. |
Many LLM evaluation frameworks offer flexibility to accommodate domain-specific or custom evaluations, addressing the key RAG metrics for your use case. These frameworks utilize either LLM-as-a-Judge or the OpenAI Moderation API to ensure the moderation of responses from your AI applications.
Working with custom datasets

First, create question and ground-truth answer pairs from source documents for the evaluation dataset. Ground-truth answers are the precise responses you expect from the RAG system. You can create these in multiple ways:
- Hand-crafting your dataset: Manually create questions and answers.
- Use LLM to create synthetic data: Leverage LLMs like T5 or OpenAI APIs.
- Use the Ragas framework: This method uses an LLM to generate various question types for evaluating RAG systems.
- Use FiddleCube: FiddleCube is a system that can help generate a range of question types aimed at different aspects of the testing process.
Once you have created a dataset, collect the retrieved context and the final answer generated by your RAG pipeline for each question.
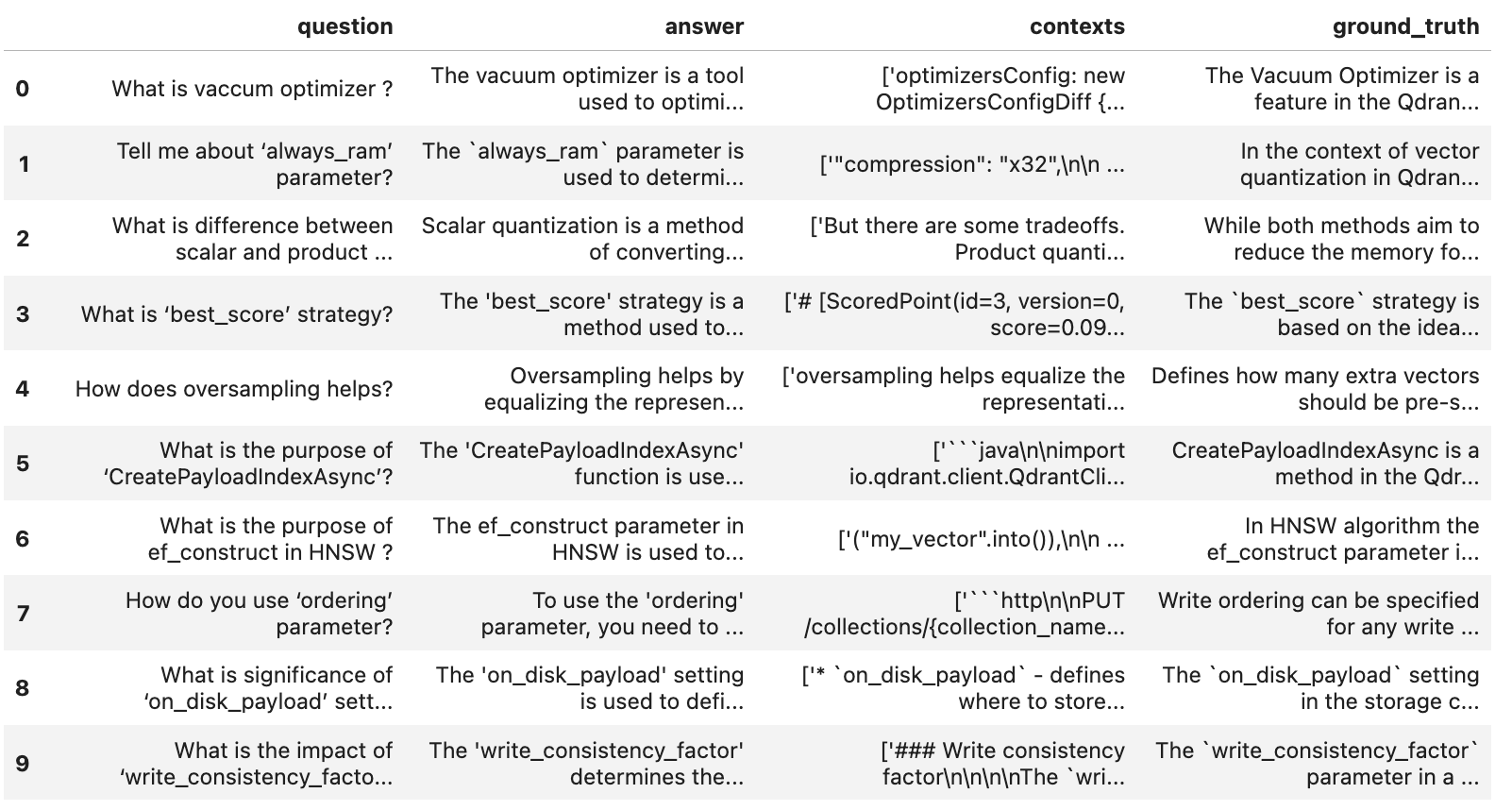
Figure 5: Here is an example of four evaluation metrics:
- question: A set of questions based on the source document.
- ground_truth: The anticipated accurate answers to the queries.
- context: The context retrieved by the RAG pipeline for each query.
- answer: The answer generated by the RAG pipeline for each query.
Conclusion: What to look for when running tests
To understand if a RAG system is functioning as it should, you want to ensure:
- Retrieval effectiveness: The information retrieved is semantically relevant.
- Relevance of responses: The generated response is meaningful.
- Coherence of generated responses: The response is coherent and logically connected.
- Up-to-date responses: The response is based on current data.
Evaluating a RAG application from End-to-End (E2E)
The End-to-End (E2E) evaluation assesses the overall performance of the entire Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system. Here are some of the key factors you can measure:
- Helpfulness: Measures how well the system’s responses assist users in achieving their goals.
- Groundedness: Ensures that the responses are based on verifiable information from the retrieved context.
- Latency: Monitors the response time of the system to ensure it meets the required speed and efficiency standards.
- Conciseness: Evaluates whether the responses are brief yet comprehensive.
- Consistency: Ensures that the system consistently delivers high-quality responses across different queries and contexts.
For instance, you can measure the quality of the generated responses with metrics like Answer Semantic Similarity and Correctness.
Measuring semantic similarity will tell you the difference between the generated answer and the ground truth, ranging from 0 to 1. This system cosine similarity to evaluate alignment in the vector space.
Checking answer correctness evaluates the overall agreement between the generated answer and the ground truth, combining factual correctness (measured by the F1 score) and answer similarity score.
RAG evaluation is just the beginning

RAG evaluation is just the beginning. It lays the foundation for continuous improvement and long-term success of your system. Initially, it can help you identify and address immediate issues related to retrieval accuracy, contextual relevance, and response quality. However, as your RAG system evolves and is subjected to new data, use cases, and user interactions, you need to continue testing and calibrating.
By continuously evaluating your application, you can ensure that the system adapts to changing requirements and maintains its performance over time. You should regularly calibrate all components such as embedding models, retrieval algorithms, and the LLM itself. This iterative process will help you identify and fix emerging problems, optimize system parameters, and incorporate user feedback.
The practice of RAG evaluation is in the early stages of development. Keep this guide and wait as more techniques, models, and evaluation frameworks are developed. We strongly recommend you incorporate them into your evaluation process.
Want to download a printer-friendly version of this guide? Fill out this form and we will email you the PDF.
Helpful Links
- Join our community on Discord
- Check out our latest articles
- Try a free Qdrant cluster
- Choose the right deployment option for your application. Talk to sales




































