Inference
Inference is the process of using a machine learning model to create vector embeddings from text, images, or other data types. While you can create embeddings on the client side, you can also let Qdrant generate them while storing or querying data.
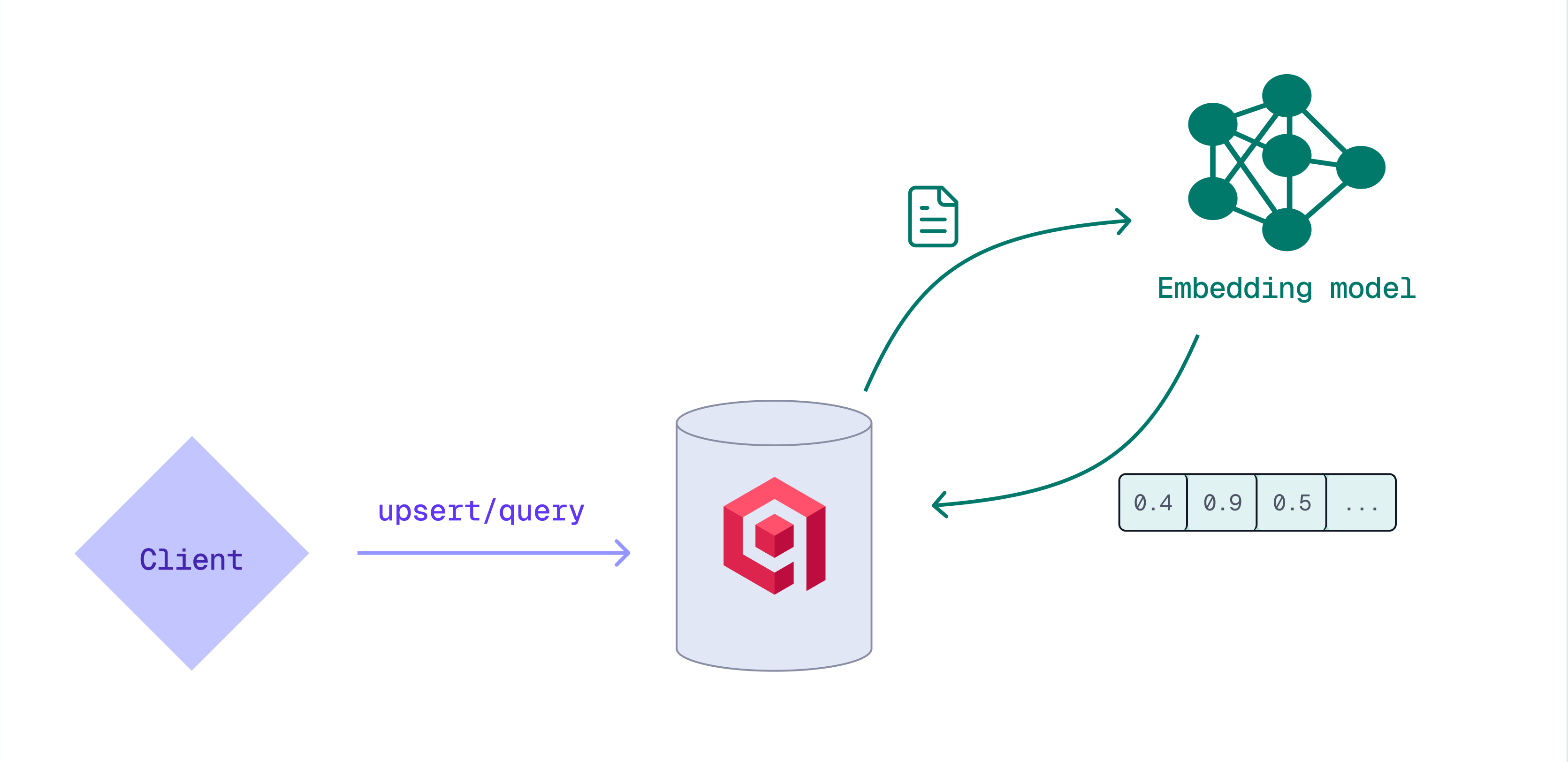
There are several advantages to generating embeddings with Qdrant:
- No need for external pipelines or separate model servers.
- Work with a single unified API instead of a different API per model provider.
- No external network calls, minimizing delays or data transfer overhead.
Depending on the model you want to use, inference can be executed:
- on the client side, using the FastEmbed library
- by the Qdrant cluster (only supported for the BM25 model)
- in Qdrant Cloud, using Cloud Inference (for clusters on Qdrant Managed Cloud)
- externally (models by OpenAI, Cohere, and Jina AI; for clusters on Qdrant Managed Cloud)
Inference API
You can use inference in the API wherever you can use regular vectors. Instead of a vector, you can use special Inference Objects:
Documentobject, used for text inference// Document { // Text input text: "Your text", // Name of the model, to do inference with model: "<the-model-to-use>", // Extra parameters for the model, Optional options: {} }Imageobject, used for image inference// Image { // Image input image: "<url>", // Or base64 encoded image // Name of the model, to do inference with model: "<the-model-to-use>", // Extra parameters for the model, Optional options: {} }Objectobject, reserved for other types of input, which might be implemented in the future.
The Qdrant API supports the usage of these Inference Objects in all places where regular vectors can be used. For example:
POST /collections/<your-collection>/points/query
{
"query": {
"nearest": [0.12, 0.34, 0.56, 0.78, ...]
}
}
Can be replaced with
POST /collections/<your-collection>/points/query
{
"query": {
"nearest": {
"text": "My Query Text",
"model": "<the-model-to-use>"
}
}
}
In this case, Qdrant uses the configured embedding model to automatically create a vector from the Inference Object and then perform the search query with it. All of this happens within a low-latency network.
Server-side Inference: BM25
BM25 (Best Matching 25) is a ranking function for text search. BM25 uses sparse vectors that represent documents, where each dimension corresponds to a word. Qdrant can generate these sparse embeddings from input text directly on the server.
While upserting points, provide the text and the qdrant/bm25 embedding model:
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/points
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"vector": {
"my-bm25-vector": {
"text": "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
"model": "qdrant/bm25"
}
}
}
]
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.upsert(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
points=[
models.PointStruct(
id=1,
vector={
"my-bm25-vector": models.Document(
text="Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
model="Qdrant/bm25",
)
},
)
],
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.upsert("{collection_name}", {
points: [
{
id: 1,
vector: {
'my-bm25-vector': {
text: 'Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies',
model: 'Qdrant/bm25',
},
},
},
],
});
use qdrant_client::{
Payload, Qdrant,
qdrant::{DocumentBuilder, PointStruct, UpsertPointsBuilder},
};
use std::collections::HashMap;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("<your-qdrant-url>").build()?;
client
.upsert_points(UpsertPointsBuilder::new(
"{collection_name}",
vec![PointStruct::new(
1,
HashMap::from([(
"my-bm25-vector".to_string(),
DocumentBuilder::new("Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies", "qdrant/bm25")
.build(),
)]),
Payload::default(),
)],
))
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorFactory.vector;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorsFactory.namedVectors;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Image;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PointStruct;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.upsertAsync(
"{collection_name}",
List.of(
PointStruct.newBuilder()
.setId(id(1))
.setVectors(
namedVectors(
Map.of(
"my-bm25-vector",
vector(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("qdrant/bm25")
.setText("Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies")
.build()))))
.build()))
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io", port: 6334, https: true, apiKey: "<your-api-key>");
await client.UpsertAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
points: new List<PointStruct>
{
new()
{
Id = 1,
Vectors = new Dictionary<string, Vector>
{
["my-bm25-vector"] = new Document()
{
Model = "qdrant/bm25",
Text = "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
},
},
},
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Upsert(context.Background(), &qdrant.UpsertPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Points: []*qdrant.PointStruct{
{
Id: qdrant.NewIDNum(uint64(1)),
Vectors: qdrant.NewVectorsMap(map[string]*qdrant.Vector{
"my-bm25-vector": qdrant.NewVectorDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "qdrant/bm25",
Text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
}),
}),
},
},
})
Qdrant uses the model to generate the embeddings and stores the point with the resulting vector. Retrieving the point shows the embeddings that were generated:
....
"my-bm25-vector": {
"indices": [
112174620,
177304315,
662344706,
771857363,
1617337648
],
"values": [
1.6697302,
1.6697302,
1.6697302,
1.6697302,
1.6697302
]
}
....
]
Similarly, you can use inference at query time by providing the text to query with as well as the embedding model:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"text": "How to bake cookies?",
"model": "qdrant/bm25"
},
"using": "my-bm25-vector"
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.Document(
text="How to bake cookies?",
model="Qdrant/bm25",
),
using="my-bm25-vector",
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
text: 'How to bake cookies?',
model: 'qdrant/bm25',
},
using: 'my-bm25-vector',
});
use qdrant_client::{
Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, Query, QueryPointsBuilder},
};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("<your-qdrant-url>").build().unwrap();
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_nearest(Document {
text: "How to bake cookies?".into(),
model: "qdrant/bm25".into(),
..Default::default()
}))
.using("my-bm25-vector")
.build(),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.queryAsync(
Points.QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(
nearest(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("qdrant/bm25")
.setText("How to bake cookies?")
.build()))
.setUsing("my-bm25-vector")
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
port: 6334,
https: true,
apiKey: "<your-api-key>"
);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new Document() { Model = "qdrant/bm25", Text = "How to bake cookies?" },
usingVector: "my-bm25-vector"
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryNearest(
qdrant.NewVectorInputDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "qdrant/bm25",
Text: "How to bake cookies?",
}),
),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("my-bm25-vector"),
})
Qdrant Cloud Inference
Clusters on Qdrant Managed Cloud can access embedding models that are hosted on Qdrant Cloud. For a list of available models, visit the Inference tab of the Cluster Detail page in the Qdrant Cloud Console. Here, you can also enable Cloud Inference for a cluster if it’s not already enabled.
Before using a Cloud-hosted embedding model, ensure that your collection has been configured for vectors with the correct dimensionality. The Inference tab of the Cluster Detail page in the Qdrant Cloud Console lists the dimensionality for each supported embedding model.
Text Inference
Let’s consider an example of using Cloud Inference with a text model that produces dense vectors. This example creates one point and uses a simple search query with a Document Inference Object.
# Insert new points with cloud-side inference
PUT /collections/<your-collection>/points?wait=true
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"payload": { "topic": "cooking", "type": "dessert" },
"vector": {
"text": "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
"model": "<the-model-to-use>"
}
}
]
}
# Search in the collection using cloud-side inference
POST /collections/<your-collection>/points/query
{
"query": {
"text": "How to bake cookies?",
"model": "<the-model-to-use>"
}
}
# Create a new vector
curl -X PUT "https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333/collections/<your-collection>/points?wait=true" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "api-key: <paste-your-api-key-here>" \
-d '{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"payload": { "topic": "cooking", "type": "dessert" },
"vector": {
"text": "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
"model": "<the-model-to-use>"
}
}
]
}'
# Perform a search query
curl -X POST "https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333/collections/<your-collection>/points/query" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "api-key: <paste-your-api-key-here>" \
-d '{
"query": {
"text": "How to bake cookies?",
"model": "<the-model-to-use>"
}
}'
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient
from qdrant_client.models import PointStruct, Document
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<paste-your-api-key-here>",
# IMPORTANT
# If not enabled, inference will be performed locally
cloud_inference=True,
)
points = [
PointStruct(
id=1,
payload={"topic": "cooking", "type": "dessert"},
vector=Document(
text="Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
model="<the-model-to-use>"
)
)
]
client.upsert(collection_name="<your-collection>", points=points)
result = client.query_points(
collection_name="<your-collection>",
query=Document(
text="How to bake cookies?",
model="<the-model-to-use>"
)
)
print(result)
import {QdrantClient} from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({
url: 'https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333',
apiKey: '<paste-your-api-key-here>',
});
const points = [
{
id: 1,
payload: { topic: "cooking", type: "dessert" },
vector: {
text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
model: "<the-model-to-use>"
}
}
];
await client.upsert("<your-collection>", { wait: true, points });
const result = await client.query(
"<your-collection>",
{
query: {
text: "How to bake cookies?",
model: "<the-model-to-use>"
},
}
)
console.log(result);
use qdrant_client::qdrant::Query;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::QueryPointsBuilder;
use qdrant_client::Payload;
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Document};
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{PointStruct, UpsertPointsBuilder};
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6334")
.api_key("<paste-your-api-key-here>")
.build()
.unwrap();
let points = vec![
PointStruct::new(
1,
Document::new(
"Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
"<the-model-to-use>"
),
Payload::try_from(serde_json::json!(
{"topic": "cooking", "type": "dessert"}
)).unwrap(),
)
];
let upsert_request = UpsertPointsBuilder::new(
"<your-collection>",
points
).wait(true);
let _ = client.upsert_points(upsert_request).await;
let query_document = Document::new(
"How to bake cookies?",
"<the-model-to-use>"
);
let query_request = QueryPointsBuilder::new("<your-collection>")
.query(Query::new_nearest(query_document));
let result = client.query(query_request).await.unwrap();
println!("Result: {:?}", result);
}
package org.example;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorsFactory.vectors;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PointStruct;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<paste-your-api-key-here>")
.build());
client
.upsertAsync(
"<your-collection>",
List.of(
PointStruct.newBuilder()
.setId(id(1))
.setVectors(
vectors(
Document.newBuilder()
.setText("Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies")
.setModel("<the-model-to-use>")
.build()))
.putAllPayload(Map.of("topic", value("cooking"), "type", value("dessert")))
.build()))
.get();
List <Points.ScoredPoint> points =
client
.queryAsync(
Points.QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("<your-collection>")
.setQuery(
nearest(
Document.newBuilder()
.setText("How to bake cookies?")
.setModel("<the-model-to-use>")
.build()))
.build())
.get();
System.out.printf(points.toString());
}
}
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using Value = Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Value;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
port: 6334,
https: true,
apiKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>"
);
await client.UpsertAsync(
collectionName: "<your-collection>",
points: new List <PointStruct> {
new() {
Id = 1,
Vectors = new Document() {
Text = "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
Model = "<the-model-to-use>",
},
Payload = {
["topic"] = "cooking",
["type"] = "dessert"
},
},
}
);
var points = await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "<your-collection>",
query: new Document() {
Text = "How to bake cookies?",
Model = "<the-model-to-use>"
}
);
foreach(var point in points) {
Console.WriteLine(point);
}
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"time"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
func main() {
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second)
defer cancel()
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)
}
defer client.Close()
_, err = client.Upsert(ctx, &qdrant.UpsertPoints{
CollectionName: "<your-collection>",
Points: []*qdrant.PointStruct{
{
Id: qdrant.NewIDNum(1),
Vectors: qdrant.NewVectorsDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
Model: "<the-model-to-use>",
}),
Payload: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"topic": "cooking",
"type": "dessert",
}),
},
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error creating point: %v", err)
}
points, err := client.Query(ctx, &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "<your-collection>",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryNearest(
qdrant.NewVectorInputDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Text: "How to bake cookies?",
Model: "<the-model-to-use>",
}),
),
})
log.Printf("List of points: %s", points)
}
Usage examples, specific to each cluster and model, can also be found in the Inference tab of the Cluster Detail page in the Qdrant Cloud Console.
Note that each model has a context window, which is the maximum number of tokens that can be processed by the model in a single request. If the input text exceeds the context window, it is truncated to fit within the limit. The context window size is displayed in the Inference tab of the Cluster Detail page.
For dense vector models, you also have to ensure that the vector size configured in the collection matches the output size of the model. If the vector size does not match, the upsert will fail with an error.
Image Inference
Here is another example of using Cloud Inference with an image model. This example uses the CLIP model to encode an image and then uses a text query to search for it.
Since the CLIP model is multimodal, we can use both image and text inputs on the same vector field.
# Insert new points with cloud-side inference
PUT /collections/<your-collection>/points?wait=true
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"vector": {
"image": "https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
"model": "qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-vision"
},
"payload": {
"title": "Example Image"
}
}
]
}
# Search in the collection using cloud-side inference
POST /collections/<your-collection>/points/query
{
"query": {
"text": "Mission to Mars",
"model": "qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-text"
}
}
# Create a new vector
curl -X PUT "https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333/collections/<your-collection>/points?wait=true" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "api-key: <paste-your-api-key-here>" \
-d '{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"vector": {
"image": "https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
"model": "qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-vision"
},
"payload": {
"title": "Example Image"
}
}
]
}'
# Perform a search query
curl -X POST "https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333/collections/<your-collection>/points/query" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "api-key: <paste-your-api-key-here>" \
-d '{
"query": {
"text": "Mission to Mars",
"model": "qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-text"
}
}'
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient
from qdrant_client.models import PointStruct, Image, Document
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<paste-your-api-key-here>",
# IMPORTANT
# If not enabled, inference will be performed locally
cloud_inference=True,
)
points = [
PointStruct(
id=1,
vector=Image(
image="https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
model="qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-vision"
),
payload={
"title": "Example Image"
}
)
]
client.upsert(collection_name="<your-collection>", points=points)
result = client.query_points(
collection_name="<your-collection>",
query=Document(
text="Mission to Mars",
model="qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-text"
)
)
print(result)
import {QdrantClient} from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({
url: 'https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333',
apiKey: '<paste-your-api-key-here>',
});
const points = [
{
id: 1,
vector: {
image: "https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
model: "qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-vision"
},
payload: {
title: "Example Image"
}
}
];
await client.upsert("<your-collection>", { wait: true, points });
const result = await client.query(
"<your-collection>",
{
query: {
text: "Mission to Mars",
model: "qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-text"
},
}
)
console.log(result);
use qdrant_client::qdrant::Query;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::QueryPointsBuilder;
use qdrant_client::Payload;
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Document, Image};
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{PointStruct, UpsertPointsBuilder};
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6334")
.api_key("<paste-your-api-key-here>")
.build()
.unwrap();
let points = vec![
PointStruct::new(
1,
Image::new_from_url(
"https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
"qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-vision"
),
Payload::try_from(serde_json::json!({
"title": "Example Image"
})).unwrap(),
)
];
let upsert_request = UpsertPointsBuilder::new(
"<your-collection>",
points
).wait(true);
let _ = client.upsert_points(upsert_request).await;
let query_document = Document::new(
"Mission to Mars",
"qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-text"
);
let query_request = QueryPointsBuilder::new("<your-collection>")
.query(Query::new_nearest(query_document));
let result = client.query(query_request).await.unwrap();
println!("Result: {:?}", result);
}
package org.example;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorsFactory.vectors;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Image;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PointStruct;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<paste-your-api-key-here>")
.build());
client
.upsertAsync(
"<your-collection>",
List.of(
PointStruct.newBuilder()
.setId(id(1))
.setVectors(
vectors(
Image.newBuilder()
.setImage(value("https://qdrant.tech/example.png"))
.setModel("qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-vision")
.build()))
.putAllPayload(Map.of("title", value("Example Image")))
.build()))
.get();
List <Points.ScoredPoint> points =
client
.queryAsync(
Points.QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("<your-collection>")
.setQuery(
nearest(
Document.newBuilder()
.setText("Mission to Mars")
.setModel("qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-text")
.build()))
.build())
.get();
System.out.printf(points.toString());
}
}
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using Value = Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Value;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
port: 6334,
https: true,
apiKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>"
);
await client.UpsertAsync(
collectionName: "<your-collection>",
points: new List <PointStruct> {
new() {
Id = 1,
Vectors = new Image() {
Image_ = "https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
Model = "qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-vision",
},
Payload = {
["title"] = "Example Image"
},
},
}
);
var points = await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "<your-collection>",
query: new Document() {
Text = "Mission to Mars",
Model = "qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-text"
}
);
foreach(var point in points) {
Console.WriteLine(point);
}
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"time"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
func main() {
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second)
defer cancel()
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)
}
defer client.Close()
_, err = client.Upsert(ctx, &qdrant.UpsertPoints{
CollectionName: "<your-collection>",
Points: []*qdrant.PointStruct{
{
Id: qdrant.NewIDNum(1),
Vectors: qdrant.NewVectorsImage(&qdrant.Image{
Model: "qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-vision",
Image: qdrant.NewValueString("https://qdrant.tech/example.png"),
}),
Payload: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"title": "Example image",
}),
},
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error creating point: %v", err)
}
points, err := client.Query(ctx, &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "<your-collection>",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryNearest(
qdrant.NewVectorInputDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Text: "Mission to Mars",
Model: "qdrant/clip-vit-b-32-text",
}),
),
})
log.Printf("List of points: %s", points)
}
The Qdrant Cloud Inference server will download the images using the provided URL. Alternatively, you can provide the image as a base64-encoded string. Each model has limitations on the file size and extensions it can work with. Refer to the model card for details.
Local Inference Compatibility
The Python SDK offers a unique capability: it supports both local and cloud inference through an identical interface.
You can easily switch between local and cloud inference by setting the cloud_inference flag when initializing the QdrantClient. For example:
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://your-cluster.qdrant.io",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True, # Set to False to use local inference
)
This flexibility allows you to develop and test your applications locally or in continuous integration (CI) environments without requiring access to cloud inference resources.
- When
cloud_inferenceis set toFalse, inference is performed locally usingfastembed. - When set to
True, inference requests are handled by Qdrant Cloud.
External Embedding Model Providers
Qdrant Cloud can act as a proxy for the APIs of external embedding model providers:
- OpenAI
- Cohere
- Jina AI
- OpenRouter
This enables you to access any of the embedding models provided by these providers through the Qdrant API.
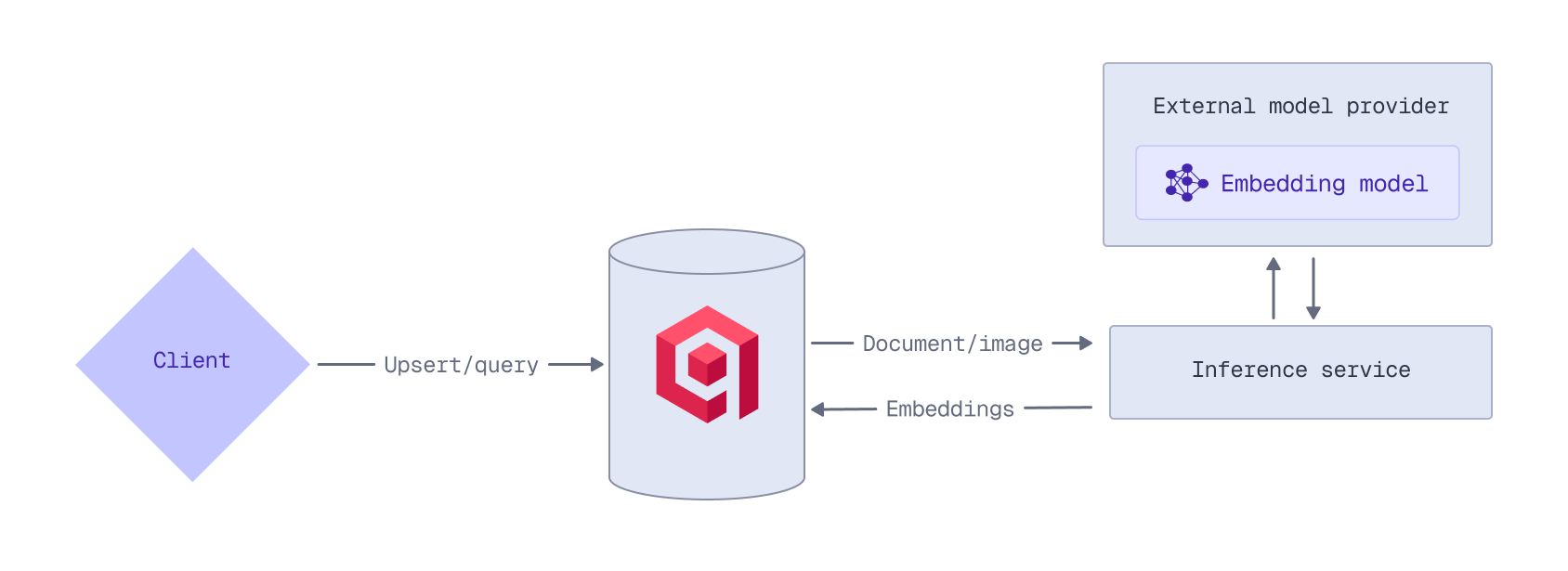
To use an external provider’s embedding model, you need an API key from that provider. For example, to access OpenAI models, you need an OpenAI API key. Qdrant does not store or cache your API keys; they must be provided with each inference request.
When using an external embedding model, ensure that your collection has been configured for vectors with the correct dimensionality. Refer to the model’s documentation for details on the output dimensions.
OpenAI
When you prepend a model name with openai/, the embedding request is automatically routed to the OpenAI Embeddings API.
For example, to use OpenAI’s text-embedding-3-large model when ingesting data, prepend the model name with openai/ and provide your OpenAI API key in the options object. Any OpenAI-specific API parameters can be passed using the options object. This example uses the OpenAI-specific API dimensions parameter to reduce the dimensionality to 512:
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/points?wait=true
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"vector": {
"text": "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
"model": "openai/text-embedding-3-large",
"options": {
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"dimensions": 512
}
}
}
]
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.upsert(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
points=[
models.PointStruct(
id=1,
vector=models.Document(
text="Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
model="openai/text-embedding-3-large",
options={
"openai-api-key": "<your_openai_api_key>",
"dimensions": 512
}
)
)
]
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.upsert("{collection_name}", {
points: [
{
id: 1,
vector: {
text: 'Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies',
model: 'openai/text-embedding-3-large',
options: {
'openai-api-key': '<your_openai_api_key>',
dimensions: 512,
},
},
},
],
});
use qdrant_client::{
Payload, Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, PointStruct, UpsertPointsBuilder},
};
use std::collections::HashMap;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("<your-qdrant-url>").build()?;
let mut options = HashMap::new();
options.insert("openai-api-key".to_string(), "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>".into());
options.insert("dimensions".to_string(), 512.into());
client
.upsert_points(UpsertPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}",
vec![
PointStruct::new(1,
Document {
text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies".into(),
model: "openai/text-embedding-3-large".into(),
options,
},
Payload::default())
]).wait(true))
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorsFactory.vectors;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PointStruct;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.upsertAsync(
"{collection_name}",
List.of(
PointStruct.newBuilder()
.setId(id(1))
.setVectors(
vectors(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("openai/text-embedding-3-large")
.setText("Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies")
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"openai-api-key",
value("<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"),
"dimensions",
value(512)))
.build()))
.build()))
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io", port: 6334, https: true, apiKey: "<your-api-key>");
await client.UpsertAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
points: new List<PointStruct>
{
new()
{
Id = 1,
Vectors = new Document()
{
Model = "openai/text-embedding-3-large",
Text = "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
Options = { ["openai-api-key"] = "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>", ["dimensions"] = 512 },
},
},
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Upsert(context.Background(), &qdrant.UpsertPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Points: []*qdrant.PointStruct{
{
Id: qdrant.NewIDNum(uint64(1)),
Vectors: qdrant.NewVectorsDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "openai/text-embedding-3-large",
Text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"dimensions": 512,
}),
}),
},
},
})
At query time, you can use the same model by prepending the model name with openai/ and providing your OpenAI API key in the options object. This example again uses the OpenAI-specific API dimensions parameter to reduce the dimensionality to 512:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"text": "How to bake cookies?",
"model": "openai/text-embedding-3-large",
"options": {
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"dimensions": 512
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.Document(
text="How to bake cookies?",
model="openai/text-embedding-3-large",
options={
"openai-api-key": "<your_openai_api_key>",
"dimensions": 512
}
)
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
text: 'How to bake cookies?',
model: 'openai/text-embedding-3-large',
options: {
'openai-api-key': '<your_openai_api_key>',
dimensions: 512,
},
},
});
use qdrant_client::{
Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, Query, QueryPointsBuilder, Value},
};
use std::collections::HashMap;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("<your-qdrant-url>").build().unwrap();
let mut options = HashMap::<String, Value>::new();
options.insert("openai-api-key".to_string(), "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>".into());
options.insert("dimensions".to_string(), 512.into());
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_nearest(Document {
text: "How to bake cookies?".into(),
model: "openai/text-embedding-3-large".into(),
options,
}))
.build(),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(
nearest(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("openai/text-embedding-3-large")
.setText("How to bake cookies?")
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"openai-api-key",
value("<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"),
"dimensions",
value(512)))
.build()))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
port: 6334,
https: true,
apiKey: "<your-api-key>"
);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new Document()
{
Model = "openai/text-embedding-3-large",
Text = "How to bake cookies?",
Options = { ["openai-api-key"] = "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>", ["dimensions"] = 512 },
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryNearest(
qdrant.NewVectorInputDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "openai/text-embedding-3-large",
Text: "How to bake cookies?",
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"dimensions": 512,
}),
}),
),
})
Note that, because Qdrant does not store or cache your OpenAI API key, you need to provide it with each inference request.
Cohere
When you prepend a model name with cohere/, the embedding request is automatically routed to the Cohere Embed API.
For example, to use Cohere’s multimodal embed-v4.0 model when ingesting data, prepend the model name with cohere/ and provide your Cohere API key in the options object. This example uses the Cohere-specific API output_dimension parameter to reduce the dimensionality to 512:
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/points?wait=true
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"vector": {
"image": "data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAoAAAAKCAYAAACNMs+9AAAAFUlEQVR42mNk+M9Qz0AEYBxVSF+FAAhKDveksOjmAAAAAElFTkSuQmCC",
"model": "cohere/embed-v4.0",
"options": {
"cohere-api-key": "<YOUR_COHERE_API_KEY>",
"output_dimension": 512
}
}
}
]
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.upsert(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
points=[
models.PointStruct(
id=1,
vector=models.Document(
text="a green square",
model="cohere/embed-v4.0",
options={
"cohere-api-key": "<your_cohere_api_key>",
"output_dimension": 512
}
)
)
]
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.upsert("{collection_name}", {
points: [
{
id: 1,
vector: {
text: 'a green square',
model: 'cohere/embed-v4.0',
options: {
'cohere-api-key': '<your_cohere_api_key>',
output_dimension: 512,
},
},
},
],
});
use qdrant_client::{
Payload, Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, PointStruct, UpsertPointsBuilder},
};
use std::collections::HashMap;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("<your-qdrant-url>").build()?;
let mut options = HashMap::new();
options.insert("cohere-api-key".to_string(), "<YOUR_COHERE_API_KEY>".into());
options.insert("output_dimension".to_string(), 512.into());
client
.upsert_points(UpsertPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}",
vec![
PointStruct::new(1,
Document {
text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies requires flour, sugar, eggs, and chocolate chips.".into(),
model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small".into(),
options,
},
Payload::default())
]).wait(true))
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorsFactory.vectors;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Image;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PointStruct;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.upsertAsync(
"{collection_name}",
List.of(
PointStruct.newBuilder()
.setId(id(1))
.setVectors(
vectors(
Image.newBuilder()
.setModel("cohere/embed-v4.0")
.setImage(
value(
"data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAoAAAAKCAYAAACNMs+9AAAAFUlEQVR42mNk+M9Qz0AEYBxVSF+FAAhKDveksOjmAAAAAElFTkSuQmCC"))
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"cohere-api-key",
value("<YOUR_COHERE_API_KEY>"),
"output_dimension",
value(512)))
.build()))
.build()))
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io", port: 6334, https: true, apiKey: "<your-api-key>");
await client.UpsertAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
points: new List<PointStruct>
{
new()
{
Id = 1,
Vectors = new Image()
{
Model = "cohere/embed-v4.0",
Image_ =
"data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAoAAAAKCAYAAACNMs+9AAAAFUlEQVR42mNk+M9Qz0AEYBxVSF+FAAhKDveksOjmAAAAAElFTkSuQmCC",
Options =
{
["cohere-api-key"] = "<YOUR_COHERE_API_KEY>",
["output_dimension"] = 512,
},
},
},
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Upsert(context.Background(), &qdrant.UpsertPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Points: []*qdrant.PointStruct{
{
Id: qdrant.NewIDNum(uint64(1)),
Vectors: qdrant.NewVectorsImage(&qdrant.Image{
Model: "cohere/embed-v4.0",
Image: qdrant.NewValueString("data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAoAAAAKCAYAAACNMs+9AAAAFUlEQVR42mNk+M9Qz0AEYBxVSF+FAAhKDveksOjmAAAAAElFTkSuQmCC"),
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"cohere-api-key": "<YOUR_COHERE_API_KEY>",
"output_dimension": 512,
}),
}),
},
},
})
Note that the Cohere embed-v4.0 model does not support passing an image as a URL. You need to provide a base64-encoded image as a Data URL.
At query time, you can use the same model by prepending the model name with cohere/ and providing your Cohere API key in the options object. This example again uses the Cohere-specific API output_dimension parameter to reduce the dimensionality to 512:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"text": "a green square",
"model": "cohere/embed-v4.0",
"options": {
"cohere-api-key": "<YOUR_COHERE_API_KEY>",
"output_dimension": 512
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.Document(
text="a green square",
model="cohere/embed-v4.0",
options={
"cohere-api-key": "<your_cohere_api_key>",
"output_dimension": 512
}
)
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
text: 'a green square',
model: 'cohere/embed-v4.0',
options: {
'cohere-api-key': '<your_cohere_api_key>',
output_dimension: 512,
},
},
});
use qdrant_client::{
Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, Query, QueryPointsBuilder, Value},
};
use std::collections::HashMap;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6333").build().unwrap();
let mut options = HashMap::<String, Value>::new();
options.insert("cohere-api-key".to_string(), "<YOUR_COHERE_API_KEY>".into());
options.insert("output_dimension".to_string(), 512.into());
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_nearest(Document {
text: "a green square".into(),
model: "cohere/embed-v4.0".into(),
options,
}))
.build(),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(
nearest(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("cohere/embed-v4.0")
.setText("a green square")
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"cohere-api-key",
value("<YOUR_COHERE_API_KEY>"),
"output_dimension",
value(512)))
.build()))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
port: 6334,
https: true,
apiKey: "<your-api-key>"
);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new Document()
{
Model = "cohere/embed-v4.0",
Text = "a green square",
Options = { ["cohere-api-key"] = "<YOUR_COHERE_API_KEY>", ["output_dimension"] = 512 },
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryNearest(
qdrant.NewVectorInputDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Text: "a green square",
Model: "cohere/embed-v4.0",
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"cohere-api-key": "<YOUR_COHERE_API_KEY>",
"output_dimension": 512,
}),
}),
),
})
Note that, because Qdrant does not store or cache your Cohere API key, you need to provide it with each inference request.
Jina AI
When you prepend a model name with jinaai/, the embedding request is automatically routed to the Jina AI Embedding API.
For example, to use Jina AI’s multimodal jina-clip-v2 model when ingesting data, prepend the model name with jinaai/ and provide your Jina AI API key in the options object. This example uses the Jina AI-specific API dimensions parameter to reduce the dimensionality to 512:
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/points?wait=true
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"vector": {
"image": "https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
"model": "jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
"options": {
"jina-api-key": "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>",
"dimensions": 512
}
}
}
]
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.upsert(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
points=[
models.PointStruct(
id=1,
vector=models.Image(
image="https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
model="jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
options={
"jina-api-key": "<your_jinaai_api_key>",
"dimensions": 512
}
)
)
]
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.upsert("{collection_name}", {
points: [
{
id: 1,
vector: {
image: 'https://qdrant.tech/example.png',
model: 'jinaai/jina-clip-v2',
options: {
'jina-api-key': '<your_jinaai_api_key>',
dimensions: 512,
},
},
},
],
});
use qdrant_client::{
Payload, Qdrant,
qdrant::{Image, PointStruct, UpsertPointsBuilder},
};
use std::collections::HashMap;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("<your-qdrant-url>").build()?;
let mut options = HashMap::new();
options.insert("jina-api-key".to_string(), "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>".into());
options.insert("dimensions".to_string(), 512.into());
client
.upsert_points(UpsertPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}",
vec![
PointStruct::new(1,
Image {
image: Some("https://qdrant.tech/example.png".into()),
model: "jinaai/jina-clip-v2".into(),
options,
},
Payload::default())
]).wait(true))
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorsFactory.vectors;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Image;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PointStruct;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.upsertAsync(
"{collection_name}",
List.of(
PointStruct.newBuilder()
.setId(id(1))
.setVectors(
vectors(
Image.newBuilder()
.setModel("jinaai/jina-clip-v2")
.setImage(value("https://qdrant.tech/example.png"))
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"jina-api-key",
value("<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>"),
"dimensions",
value(512)))
.build()))
.build()))
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
port: 6334,
https: true,
apiKey: "<your-api-key>"
);
await client.UpsertAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
points: new List<PointStruct>
{
new()
{
Id = 1,
Vectors = new Document()
{
Model = "jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
Text = "Mission to Mars",
Options = { ["jina-api-key"] = "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>", ["dimensions"] = 512 },
},
},
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Upsert(context.Background(), &qdrant.UpsertPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Points: []*qdrant.PointStruct{
{
Id: qdrant.NewIDNum(uint64(1)),
Vectors: qdrant.NewVectorsImage(&qdrant.Image{
Model: "jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
Image: qdrant.NewValueString("https://qdrant.tech/example.png"),
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"jina-api-key": "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>",
"dimensions": 512,
}),
}),
},
},
})
At query time, you can use the same model by prepending the model name with jinaai/ and providing your Jina AI API key in the options object. This example again uses the Jina AI-specific API dimensions parameter to reduce the dimensionality to 512:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"text": "Mission to Mars",
"model": "jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
"options": {
"jina-api-key": "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>",
"dimensions": 512
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.Document(
text="Mission to Mars",
model="jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
options={
"jina-api-key": "<your_jinaai_api_key>",
"dimensions": 512
}
)
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
text: 'Mission to Mars',
model: 'jinaai/jina-clip-v2',
options: {
'jina-api-key': '<your_jinaai_api_key>',
dimensions: 512,
},
},
});
use qdrant_client::{
Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, Query, QueryPointsBuilder, Value},
};
use std::collections::HashMap;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("<your-qdrant-url>").build().unwrap();
let mut options = HashMap::<String, Value>::new();
options.insert("jina-api-key".to_string(), "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>".into());
options.insert("dimensions".to_string(), 512.into());
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_nearest(Document {
text: "Mission to Mars".into(),
model: "jinaai/jina-clip-v2".into(),
options,
}))
.build(),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(
nearest(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("jinaai/jina-clip-v2")
.setText("Mission to Mars")
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"jina-api-key",
value("<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>"),
"dimensions",
value(512)))
.build()))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
port: 6334,
https: true,
apiKey: "<your-api-key>"
);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new Document()
{
Model = "jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
Text = "Mission to Mars",
Options = { ["jina-api-key"] = "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>", ["dimensions"] = 512 },
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryNearest(
qdrant.NewVectorInputDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Text: "Mission to Mars",
Model: "jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"jina-api-key": "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>",
"dimensions": 512,
}),
}),
),
})
Note that, because Qdrant does not store or cache your Jina AI API key, you need to provide it with each inference request
OpenRouter
OpenRouter is a platform that provides several embedding models. To use one of the models provided by the OpenRouter Embeddings API, prepend the model name with openrouter/.
For example, to use the mistralai/mistral-embed-2312 model when ingesting data, prepend the model name with openrouter/ and provide your OpenRouter API key in the options object.
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/points?wait=true
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"vector": {
"text": "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
"model": "openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312",
"options": {
"openrouter-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENROUTER_API_KEY>"
}
}
}
]
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.upsert(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
points=[
models.PointStruct(
id=1,
vector=models.Document(
text="Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
model="openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312",
options={
"openrouter-api-key": "<your_openrouter_api_key>"
}
)
)
]
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.upsert("{collection_name}", {
points: [
{
id: 1,
vector: {
text: 'Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies',
model: 'openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312',
options: {
'openrouter-api-key': '<your_openrouter_api_key>',
},
},
},
],
});
use qdrant_client::{
Payload, Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, PointStruct, UpsertPointsBuilder},
};
use std::collections::HashMap;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("<your-qdrant-url>").build()?;
let mut options = HashMap::new();
options.insert("openrouter-api-key".to_string(), "<YOUR_OPENROUTER_API_KEY>".into());
client
.upsert_points(UpsertPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}",
vec![
PointStruct::new(1,
Document {
text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies".into(),
model: "openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312".into(),
options,
},
Payload::default())
]).wait(true))
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorsFactory.vectors;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PointStruct;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-openrouter-key>")
.build());
client
.upsertAsync(
"{collection_name}",
List.of(
PointStruct.newBuilder()
.setId(id(1))
.setVectors(
vectors(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312")
.setText("Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies")
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"openrouter-api-key",
value("<YOUR_OPENROUTER_API_KEY>")))
.build()))
.build()))
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io", port: 6334, https: true, apiKey: "<your-openrouter-key>");
await client.UpsertAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
points: new List<PointStruct>
{
new()
{
Id = 1,
Vectors = new Document()
{
Model = "openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312",
Text = "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
Options = { ["openrouter-api-key"] = "<YOUR_OPENROUTER_API_KEY>" },
},
},
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-openrouter-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Upsert(context.Background(), &qdrant.UpsertPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Points: []*qdrant.PointStruct{
{
Id: qdrant.NewIDNum(uint64(1)),
Vectors: qdrant.NewVectorsDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312",
Text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"openrouter-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENROUTER_API_KEY>",
}),
}),
},
},
})
At query time, you can use the same model by prepending the model name with openrouter/ and providing your OpenRouter API key in the options object:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"text": "How to bake cookies?",
"model": "openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312",
"options": {
"openrouter-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENROUTER_API_KEY>"
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.Document(
text="How to bake cookies?",
model="openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312",
options={
"openrouter-api-key": "<your_openrouter_api_key>"
}
)
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
text: 'How to bake cookies?',
model: 'openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312',
options: {
'openrouter-api-key': '<your_openrouter_api_key>'
},
},
});
use qdrant_client::{
Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, Query, QueryPointsBuilder, Value},
};
use std::collections::HashMap;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("<your-qdrant-url>").build().unwrap();
let mut options = HashMap::<String, Value>::new();
options.insert("openrouter-api-key".to_string(), "<YOUR_OPENROUTER_API_KEY>".into());
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_nearest(Document {
text: "How to bake cookies?".into(),
model: "openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312".into(),
options,
}))
.build(),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-openrouter-key>")
.build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(
nearest(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312")
.setText("How to bake cookies?")
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"openrouter-api-key",
value("<YOUR_OPENROUTER_API_KEY>")))
.build()))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
port: 6334,
https: true,
apiKey: "<your-openrouter-key>"
);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new Document()
{
Model = "openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312",
Text = "How to bake cookies?",
Options = { ["openrouter-api-key"] = "<YOUR_OPENROUTER_API_KEY>" },
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-openrouter-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryNearest(
qdrant.NewVectorInputDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "openrouter/mistralai/mistral-embed-2312",
Text: "How to bake cookies?",
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"openrouter-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENROUTER_API_KEY>",
}),
}),
),
})
Note that, because Qdrant does not store or cache your OpenRouter API key, you need to provide it with each inference request.
Multiple Inference Operations
You can run multiple inference operations within a single request, even when models are hosted in different locations. This example generates three different named vectors for a single point: image embeddings using jina-clip-v2 hosted by Jina AI, text embeddings using all-minilm-l6-v2 hosted by Qdrant Cloud, and BM25 embeddings using the bm25 model executed locally by the Qdrant cluster:
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/points?wait=true
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"vector": {
"image": {
"image": "https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
"model": "jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
"options": {
"jina-api-key": "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>",
"dimensions": 512
}
},
"text": {
"text": "Mars, the red planet",
"model": "sentence-transformers/all-minilm-l6-v2"
},
"bm25": {
"text": "Mars, the red planet",
"model": "qdrant/bm25"
}
}
}
]
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.upsert(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
points=[
models.PointStruct(
id=1,
vector={
"image": models.Image(
image="https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
model="jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
options={
"jina-api-key": "<your_jinaai_api_key>",
"dimensions": 512
},
),
"text": models.Document(
text="Mars, the red planet",
model="sentence-transformers/all-minilm-l6-v2",
),
"bm25": models.Document(
text="Mars, the red planet",
model="Qdrant/bm25",
),
},
)
],
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.upsert("{collection_name}", {
points: [
{
id: 1,
vector: {
image: {
image: 'https://qdrant.tech/example.png',
model: 'jinaai/jina-clip-v2',
options: {
'jina-api-key': '<your_jinaai_api_key>',
dimensions: 512,
},
},
text: {
text: 'Mars, the red planet',
model: 'sentence-transformers/all-minilm-l6-v2',
},
bm25: {
text: 'Mars, the red planet',
model: 'Qdrant/bm25',
},
},
},
],
});
use qdrant_client::{
Payload, Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, Image, NamedVectors, PointStruct, UpsertPointsBuilder},
};
use std::collections::HashMap;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("<your-qdrant-url>").build()?;
let mut jina_options = HashMap::new();
jina_options.insert("jina-api-key".to_string(), "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>".into());
jina_options.insert("dimensions".to_string(), 512.into());
client
.upsert_points(
UpsertPointsBuilder::new(
"{collection_name}",
vec![PointStruct::new(
1,
NamedVectors::default()
.add_vector(
"image",
Image {
image: Some("https://qdrant.tech/example.png".into()),
model: "jinaai/jina-clip-v2".into(),
options: jina_options,
},
)
.add_vector(
"text",
Document {
text: "Mars, the red planet".into(),
model: "sentence-transformers/all-minilm-l6-v2".into(),
..Default::default()
},
)
.add_vector(
"bm25",
Document {
text: "How to bake cookies?".into(),
model: "qdrant/bm25".into(),
..Default::default()
},
),
Payload::default(),
)],
)
.wait(true),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorFactory.vector;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorsFactory.namedVectors;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Image;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PointStruct;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.upsertAsync(
"{collection_name}",
List.of(
PointStruct.newBuilder()
.setId(id(1))
.setVectors(
namedVectors(
Map.of(
"image",
vector(
Image.newBuilder()
.setModel("jinaai/jina-clip-v2")
.setImage(value("https://qdrant.tech/example.png"))
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"jina-api-key",
value("<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>"),
"dimensions",
value(512)))
.build()),
"text",
vector(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("sentence-transformers/all-minilm-l6-v2")
.setText("Mars, the red planet")
.build()),
"bm25",
vector(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("qdrant/bm25")
.setText("Mars, the red planet")
.build()))))
.build()))
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io", port: 6334, https: true, apiKey: "<your-api-key>");
await client.UpsertAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
points: new List<PointStruct>
{
new()
{
Id = 1,
Vectors = new Dictionary<string, Vector>
{
["image"] = new Image()
{
Model = "jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
Image_ = "https://qdrant.tech/example.png",
Options = { ["jina-api-key"] = "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>", ["dimensions"] = 512 },
},
["text"] = new Document()
{
Model = "sentence-transformers/all-minilm-l6-v2",
Text = "Mars, the red planet",
},
["bm25"] = new Document() { Model = "qdrant/bm25", Text = "Mars, the red planet" },
},
},
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Upsert(context.Background(), &qdrant.UpsertPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Points: []*qdrant.PointStruct{
{
Id: qdrant.NewIDNum(uint64(1)),
Vectors: qdrant.NewVectorsMap(map[string]*qdrant.Vector{
"image": qdrant.NewVectorImage(&qdrant.Image{
Model: "jinaai/jina-clip-v2",
Image: qdrant.NewValueString("https://qdrant.tech/example.png"),
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"jina-api-key": "<YOUR_JINAAI_API_KEY>",
"dimensions": 512,
}),
}),
"text": qdrant.NewVectorDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "sentence-transformers/all-minilm-l6-v2",
Text: "Mars, the red planet",
}),
"my-bm25-vector": qdrant.NewVectorDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "qdrant/bm25",
Text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
}),
}),
},
},
})
When specifying multiple identical inference objects in a single request, the inference service generates embeddings only once and reuses the resulting vectors. This optimization is particularly beneficial when working with external model providers, as it reduces both latency and cost.
Reduce Vector Dimensionality with Matryoshka Models
Matryoshka Representation Learning (MRL) is a technique used to train embedding models to produce vectors that can be reduced in size with minimal loss of information. On Qdrant Cloud, for supported models, you can specify the mrl parameter in the options object to reduce the vector size to the desired dimension.
MRL on Qdrant Cloud helps minimize costs and latency when you need multiple sizes of the same vector. Instead of making several inference requests for each vector size, the inference service only generates embeddings for the full-sized vector and then reduces the vector to each requested smaller size.
The following example demonstrates how to insert a point into a collection with both the original full-size vector (large) and a reduced-size vector (small):
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/points?wait=true
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"vector": {
"large": {
"text": "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
"model": "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
"options": {
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"
}
},
"small": {
"text": "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
"model": "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
"options": {
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"mrl": 64
}
}
}
}
]
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.upsert(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
points=[
models.PointStruct(
id=1,
vector={
"large": models.Document(
text="Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
model="openai/text-embedding-3-small",
options={"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"}
),
"small": models.Document(
text="Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
model="openai/text-embedding-3-small",
options={
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"mrl": 64
},
)
},
)
],
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.upsert("{collection_name}", {
points: [
{
id: 1,
vector: {
large: {
text: 'Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies',
model: 'openai/text-embedding-3-small',
options: {
'openai-api-key': '<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>',
},
},
small: {
text: 'Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies',
model: 'openai/text-embedding-3-small',
options: {
'openai-api-key': '<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>',
mrl: 64,
},
},
},
},
],
});
use std::collections::HashMap;
use qdrant_client::{
Payload, Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, NamedVectors, PointStruct, UpsertPointsBuilder, Value},
};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
client
.upsert_points(
UpsertPointsBuilder::new(
"{collection_name}",
vec![PointStruct::new(
1,
NamedVectors::default()
.add_vector(
"large",
Document {
text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies".into(),
model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small".into(),
options: HashMap::<String, Value>::from_iter(vec![(
"openai-api-key".into(),
"<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>".into(),
)]),
},
)
.add_vector(
"small",
Document {
text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies".into(),
model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small".into(),
options: HashMap::<String, Value>::from_iter(vec![
(
"openai-api-key".into(),
Value::from("<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"),
),
("mrl".into(), Value::from(64)),
]),
},
),
Payload::default(),
)],
)
.wait(true),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorFactory.vector;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorsFactory.namedVectors;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PointStruct;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.upsertAsync(
"{collection_name}",
List.of(
PointStruct.newBuilder()
.setId(id(1))
.setVectors(
namedVectors(
Map.of(
"large",
vector(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("openai/text-embedding-3-small")
.setText("Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies")
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"openai-api-key", value("<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>")))
.build()),
"small",
vector(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("openai/text-embedding-3-small")
.setText("Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies")
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"openai-api-key",
value("<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"),
"mrl",
value(64)))
.build()))))
.build()))
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
port: 6334,
https: true,
apiKey: "<your-api-key>"
);
await client.UpsertAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
points: new List<PointStruct>
{
new()
{
Id = 1,
Vectors = new Dictionary<string, Vector>
{
["large"] = new Document()
{
Model = "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
Text = "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
Options = { ["openai-api-key"] = "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>" },
},
["small"] = new Document()
{
Model = "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
Text = "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
Options = { ["openai-api-key"] = "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>", ["mrl"] = 64 },
},
},
},
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Upsert(context.Background(), &qdrant.UpsertPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Points: []*qdrant.PointStruct{
{
Id: qdrant.NewIDNum(uint64(1)),
Vectors: qdrant.NewVectorsMap(map[string]*qdrant.Vector{
"large": qdrant.NewVectorDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
Text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
}),
}),
"small": qdrant.NewVectorDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
Text: "Recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies",
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"mrl": 64,
}),
}),
}),
},
},
})
Note that, even though the request contains two inference objects, Qdrant Cloud’s inference service only makes one inference request to the OpenAI API, saving one round trip and reducing costs.
A good use case for MRL is prefetching with smaller vectors, followed by re-scoring with the original-sized vectors, effectively balancing speed and accuracy. This example first prefetches 1000 candidates using a 64-dimensional reduced vector (small) and then re-scores them using the original full-size vector (large) to return the top 10 most relevant results:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": {
"query": {
"text": "How to bake cookies?",
"model": "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
"options": {
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"mrl": 64
}
},
"using": "small",
"limit": 1000
},
"query": {
"text": "How to bake cookies?",
"model": "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
"options": {
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"
}
},
"using": "large",
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(
url="https://xyz-example.qdrant.io:6333",
api_key="<your-api-key>",
cloud_inference=True
)
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.Document(
text="How to bake cookies?",
model="openai/text-embedding-3-small",
options={"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"}
),
using="large",
limit=10,
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=models.Document(
text="How to bake cookies?",
model="openai/text-embedding-3-small",
options={
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
"mrl": 64
}
),
using="small",
limit=1000,
)
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
prefetch: {
query: {
text: "How to bake cookies?",
model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
options: {
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
mrl: 64,
}
},
using: 'small',
limit: 1000,
},
query: {
text: "How to bake cookies?",
model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
options: {
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"
}
},
using: 'large',
limit: 10,
});
use std::collections::HashMap;
use qdrant_client::{
Qdrant,
qdrant::{Document, PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder, Value},
};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(
PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest(Document {
text: "How to bake cookies?".into(),
model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small".into(),
options: HashMap::<String, Value>::from_iter(vec![
(
"openai-api-key".to_string(),
Value::from("<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"),
),
("mrl".into(), Value::from(64)),
]),
}))
.using("small")
.limit(1000_u64),
)
.query(Query::new_nearest(Document {
text: "How to bake cookies?".into(),
model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small".into(),
options: HashMap::from_iter(vec![(
"openai-api-key".into(),
"<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>".into(),
)]),
}))
.using("large")
.limit(10_u64)
.build(),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Document;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import java.util.Map;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(
QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("xyz-example.qdrant.io", 6334, true)
.withApiKey("<your-api-key")
.build());
client
.queryAsync(
Points.QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(
nearest(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("openai/text-embedding-3-small")
.setText("How to bake cookies?")
.putAllOptions(
Map.of(
"openai-api-key",
value("<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"),
"mrl",
value(64)))
.build()))
.setUsing("small")
.setLimit(1000)
.build())
.setQuery(
nearest(
Document.newBuilder()
.setModel("openai/text-embedding-3-small")
.setText("How to bake cookies?")
.putAllOptions(Map.of("openai-api-key", value("<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>")))
.build()))
.setUsing("large")
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient(
host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
port: 6334,
https: true,
apiKey: "<your-api-key>"
);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch:
[
new()
{
Query = new Document()
{
Model = "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
Text = "How to bake cookies?",
Options = { ["openai-api-key"] = "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>", ["mrl"] = 64 },
},
Using = "small",
Limit = 1000,
},
],
query: new Document()
{
Model = "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
Text = "How to bake cookies?",
Options = { ["openai-api-key"] = "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>" },
},
usingVector: "large",
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "xyz-example.qdrant.io",
Port: 6334,
APIKey: "<paste-your-api-key-here>",
UseTLS: true,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQueryNearest(
qdrant.NewVectorInputDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
Text: "How to bake cookies?",
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"mrl": 64,
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
}),
}),
),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("small"),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(1000)),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryNearest(
qdrant.NewVectorInputDocument(&qdrant.Document{
Model: "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
Text: "How to bake cookies?",
Options: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"openai-api-key": "<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>",
}),
}),
),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("large"),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(10)),
})
