Data-Driven RAG Evaluation: Testing Qdrant Apps with Relari AI
Thierry Damiba, David Myriel & Yi Zhang
·September 16, 2024

On this page:
Using Performance Metrics to Evaluate RAG Systems
Evaluating the performance of a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) application can be a complex task for developers.
To help simplify this, Qdrant has partnered with Relari to provide an in-depth RAG evaluation process.
As a vector database, Qdrant handles the data storage and retrieval, while Relari enables you to run experiments to assess how well your RAG app performs in real-world scenarios. Together, they allow for fast, iterative testing and evaluation, making it easier to keep up with your app’s development pace.

Qdrant & Relari partnered on a joint project to test RAG performance with synthetic data.
What you’ll learn
In a recent webinar, we discussed the best approaches to building and evaluating RAG systems. Relari offers tools to evaluate large language model (LLM) applications using both intrinsic and extrinsic methods. Combined with Qdrant’s powerful data storage, it creates a solid framework for evaluation.
In this post, we’ll cover two evaluation methods you can use with Qdrant and Relari, along with practical use cases. Specifically, we’ll walk you through an example that analyzes the GitLab legal policies dataset. You can follow along with the code in this Google Colab Notebook.
Key metrics for RAG evaluation: Top-K and Auto Prompt Optimization
To ensure your RAG system works well in real-world conditions, it’s crucial to focus on performance optimization. While traditional metrics like precision, recall, and rank-based methods are helpful, they aren’t always enough. Two advanced strategies for evaluating your RAG system are Top-K Parameter Optimization and Auto Prompt Optimization. These techniques help improve the chances that your model delivers the best experience for actual users.
Top-K parameter optimization
The Top-K parameter controls how many top results are shown to users. Imagine using a search engine that only shows one result per query—it might be a good result, but most users prefer having more options. On the other hand, showing too many results can overwhelm users.
For example, in a product recommendation system, the Top-K setting determines whether users see the top 3 best-selling products or 10 different options. Tuning this parameter ensures that users have enough relevant choices without feeling lost.
With Relari and Qdrant, testing different Top-K values is easy. First, we’ll build a simple RAG app with Qdrant, and then we’ll use Relari to evaluate its performance.
How to get started
Head over to Qdrant Cloud and Relari to create accounts and get your API keys. Once you have the keys, add them to your secrets in Google Colab, and you’re ready to begin!
Install dependencies
In this case, we will use Qdrant, FastEmbed, Relari, and LangChain**
!pip install relari langchain_community langchain_qdrant
!pip install unstructured rank_bm25
!pip install --upgrade nltk
Setup the environment
from google.colab import userdata
import os
os.environ['RELARI_API_KEY'] = userdata.get('RELARI_API_KEY')
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = userdata.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')
Set up Relari
from relari import RelariClient
client = RelariClient()
Create a new Relari Project
proj = client.projects.create(name="Gitlab Employee Assistant")
Defining the golden dataset
For this case study, we’ll be using the GitLab legal policies dataset, but you can easily swap in your own dataset. Datasets are critical in Relari’s approach to evaluating and improving LLM applications. The dataset serves as the “ground truth” or reference point for testing the accuracy and performance of an LLM pipeline.
Relari’s data-driven approach ensures that the evaluation is reliable and thorough. You can learn more about how Relari handles datasets here.
!wget https://ceevaldata.blob.core.windows.net/examples/gitlab/gitlab_legal_policies.zip
!unzip gitlab_legal_policies.zip -d gitlab_legal_policies
Create the dataset
Once the data is downloaded, you can create the golden dataset by running the following command. This dataset will serve as your test or ground truth for evaluation, providing a benchmark to measure the accuracy of your RAG application.
from pathlib import Path
dir = Path("gitlab_legal_policies")
task_id = client.synth.new(
project_id=proj["id"],
name="Gitlab Legal Policies",
samples=30,
files=list(dir.glob("*.txt")),
)
This will prepare the dataset for use in Relari, allowing you to evaluate your application against a known reference.
Build a simple RAG app
Now that the project is set up, let’s move on to building the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) application for evaluation. We’ll be using Qdrant for vector search, FastEmbed for embeddings, and LangChain for managing the document workflow.
Import all libraries
from langchain_community.document_loaders.directory import DirectoryLoader
from langchain_qdrant import Qdrant
from langchain_community.embeddings.fastembed import FastEmbedEmbeddings
from relari.core.types import DatasetDatum
Load and chunk data
We will use LangChain to prepare our data.
# load the document and split it into chunks
loader = DirectoryLoader("gitlab_legal_policies/")
documents = loader.load_and_split()
Now we’ll use FastEmbed, Qdrant’s built-in embedding provider, to embed our chunks.
# Initialize FastEmbedEmbeddings
embeddings = FastEmbedEmbeddings(
model_name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5", # specify the model
)
Store data in Qdrant
Finally, we’ll upload the chunks into a Qdrant collection.
# Load chunks into a Qdrant Cloud vectorstore using FastEmbedEmbeddings
db = Qdrant.from_documents(
documents,
embedding=embeddings,
url=os.environ['QDRANT_URL'], # Qdrant Cloud URL
api_key=os.environ['QDRANT_API_KEY'], # Qdrant Cloud API Key
collection_name="gitlab_legal_policies",
)
print(f"{len(documents)} chunks loaded into Qdrant Cloud vector database.")
Start logging results
Now that the data is uploaded to Qdrant, we can build a function to run different RAG pipelines over the dataset and log the results for evaluation. This will allow us to track the performance of various configurations, such as different Top-K values, and feed the results back into Relari for further analysis.
Here’s a function that logs the results from different retriever configurations:
# Prepare a function to run different RAG pipelines over the dataset and log the results
def log_retriever_results(retriever, dataset):
log = list()
for datum in dataset.data:
# First compute the result
retrieved_docs = retriever.invoke(datum["question"])
# Now log the result in Relari format
result = DatasetDatum(
label=datum["uid"],
data={"retrieved_context": [doc.page_content for doc in retrieved_docs]},
)
log.append(result)
return log
This is the power of combining Qdrant and Relari. Instead of having to build multiple applications, slowly upsert, and retrieve data, you can use both to quickly test different parameters and instantly get results. This evaluation system is built for fast, useful iteration.
Evaluate results
Now that the RAG application is built, it’s time to evaluate its performance by experimenting with different Top-K values. The Top-K parameter controls how many top results are returned to users during retrieval, and optimizing this can improve user experience and the relevance of results.
First attempt: experimenting with top-K
In this experiment, we will test various Top-K values (3, 5, 7, and 9) to see how they affect retrieval performance.
k_values = [3, 5, 7, 9] # Define the different values of top k to experiment
semantic_retrievers = {}
semantic_logs = {}
# Run the retrievers on the dataset and log retrieved chunks
for k in k_values:
retriever = db.as_retriever(search_type="similarity", search_kwargs={"k": k})
log = log_retriever_results(retriever, dataset)
semantic_retrievers[f"k_{k}"] = retriever
semantic_logs[f"k_{k}"] = log
print(f"Results on {dataset.name} by Semantic Retriever with k={k} saved!")
Send results to Relari
Once you’ve logged the results from the different Top-K experiments, you can submit them to Relari for evaluation. Relari will analyze your results using metrics like Precision/Recall and Rank-Aware methods, allowing you to compare the performance of each configuration. Here’s how to send your results to Relari:
For each Top-K configuration, we’ll submit the results to Relari and run the evaluation using appropriate metrics. This will help you benchmark the performance of your RAG system based on different values of K.
from relari import Metric
for k in k_values:
eval_name = f"Semantic Retriever Evaluation k={k}"
eval_data = semantic_logs[f"k_{k}"]
eval_info = client.evaluations.submit(
project_id=proj["id"],
dataset=dataset_info["id"],
name=eval_name,
pipeline=[Metric.PrecisionRecallF1, Metric.RankedRetrievalMetrics],
data=eval_data,
)
print(f"{eval_name} submitted!")
With our dataset, if we want the recall to be greater than 85%, we should pick a K value of at least 7.
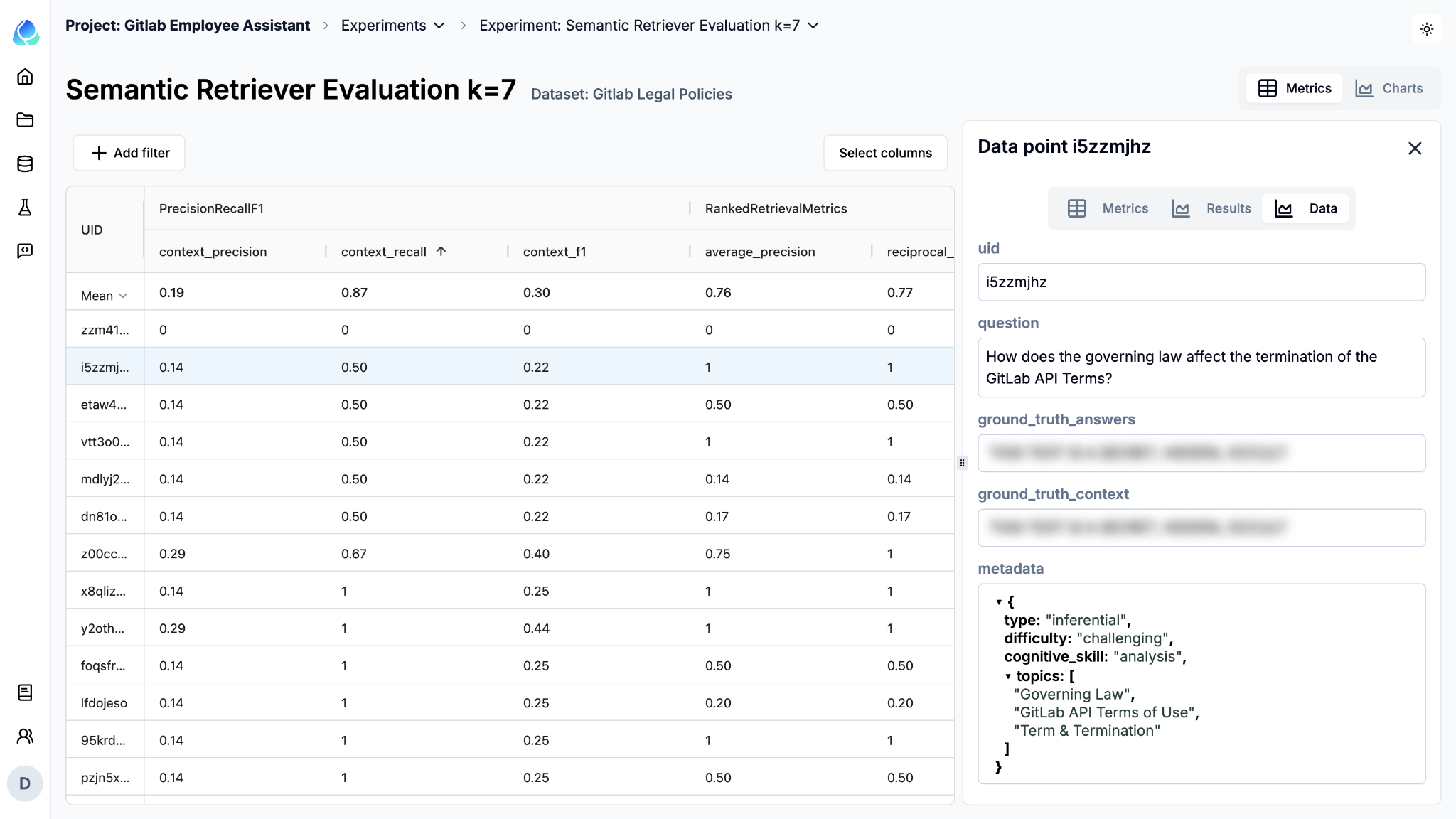
We can even look at individual cases in the UI to get more insight.
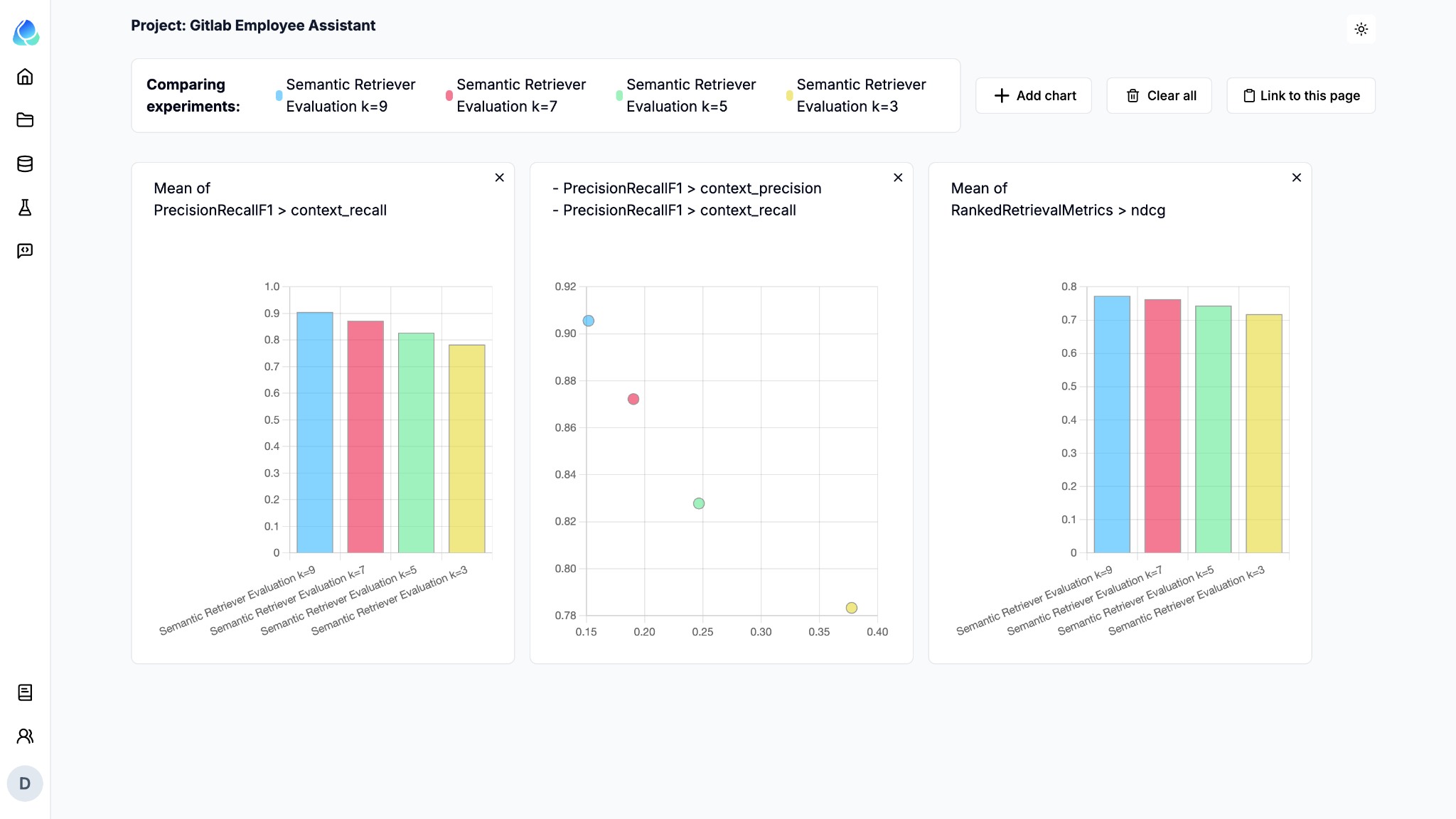
Relari and Qdrant can also be integrated to evaluate hybrid search systems, which combine both sparse (traditional keyword-based) and dense (vector-based) search methods. This combination allows you to leverage the strengths of both approaches, potentially improving the relevance and accuracy of search results.
By using Relari’s evaluation framework alongside Qdrant’s vector search capabilities, you can experiment with different configurations for hybrid search. For example, you might test varying the ratio of sparse-to-dense search results or adjust how each component contributes to the overall retrieval score.
Auto Prompt Optimization
In conversational applications like chatbots, Auto Prompt Optimization (APO) enhances the chatbot’s communication effectiveness by continuously refining how it interacts with users. APO learns from previous interactions to adjust and improve the phrasing of responses, resulting in more accurate, engaging, and user-friendly dialogues.
For instance, in a customer service chatbot, the way a question is phrased can greatly impact user satisfaction. While the same information may be conveyed, how it’s expressed matters. Think of ordering in a Parisian café: ordering in French may result in a more pleasant interaction than in English, even though the request is the same. Similarly, APO helps chatbots find the optimal way to frame questions or responses to ensure users feel understood and engaged, enhancing the overall experience.
Over time, APO fine-tunes the prompts used by the chatbot to optimize interactions, making the system more responsive to user needs and context, improving the quality of the generated answers, and ultimately increasing user satisfaction.
Auto Prompt Optimization continuously refines the chatbot’s responses to improve user interactions. Here’s how you can implement APO with Relari:
Set up base prompt
With Auto Prompt Optimization, you can define a system prompt and inspect the results at every iteration of the interaction.
from relari.core.types import Prompt, UserPrompt
base_prompt = Prompt(
system="You are a GitLab legal policy Q&A bot. Answer the following question given the context.",
user=UserPrompt(
prompt="Question: $question\n\nContext:\n$ground_truth_context",
description="Question and context to answer the question.",
),
)
The prompt uses the variablesquestion & ground_truth_context. These help measure how faithful the generated answer is to the ground truth context (i.e., it’s not hallucinating).
For more details on other metrics, visit the Relari documentation site
Set up task id
task_id = client.prompts.optimize(
name="GitLab Legal Policy RAG Prompt",
project_id=proj["id"],
dataset_id=dataset_info["id"],
prompt=base_prompt,
llm="gpt-4o-mini",
task_description="Answer the question using the provided context.",
metric=client.prompts.Metrics.CORRECTNESS,
)
print(f"Optimization task submitted with ID: {task_id}")
The CORRECTNESS metric measures how close the generated answer is the the ground truth reference answers.
Analyze Prompts
Once Auto Prompt Optimization has been set up, you can begin analyzing how the prompts evolve with each iteration in the Relari UI. This allows you to see how the system is adapting and refining its responses based on previous interactions and user feedback.
In the Relari UI, you can:
Track Changes: Review how prompts change over time and see the iterations that lead to improved performance. For example, you can analyze how different phrasings affect the accuracy and relevance of chatbot responses.
Evaluate Effectiveness: Check how each prompt performs against key metrics like correctness, fluency, and user satisfaction. You can see which iterations lead to better outcomes and which need further adjustment.
Compare Iterations: Visualize side-by-side comparisons of different prompt iterations, helping you understand which specific changes result in more accurate or engaging responses.
Identify Patterns: Look for patterns in user interactions and how the chatbot adapts to different scenarios, giving you insights into what works best for your target audience.
This prompt iteration analysis helps ensure that your chatbot’s conversational flow continually improves, leading to more natural, effective interactions with users.
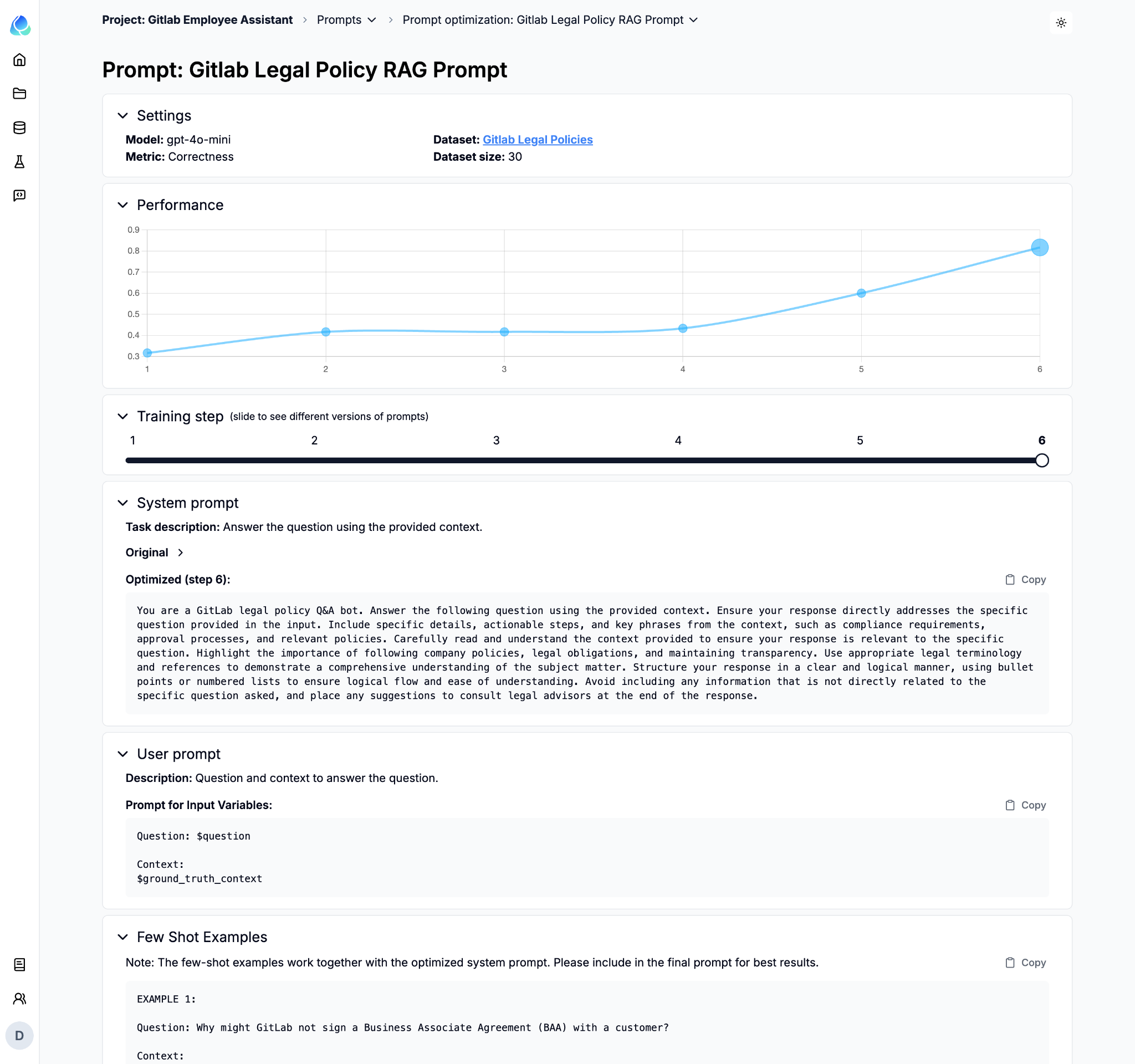
The optimal System Prompt and Few-Shot Examples generated from Auto Prompt Optimization (APO) can significantly enhance your Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system’s performance.
System Prompt: This is the foundational instruction that guides how your chatbot or application responds to user queries. APO helps refine this prompt to ensure that responses are aligned with user expectations and the application’s goal, resulting in clearer and more accurate outputs.
Few-Shot Examples: These are examples provided to the model to demonstrate how to answer a question or solve a problem. By optimizing these examples, your RAG system can better understand the context and provide more relevant and coherent responses. For example, using well-crafted few-shot examples can drastically reduce hallucinations in language model outputs and lead to more contextually accurate results.
Once you’ve identified the optimal system prompt and few-shot examples through APO, you can integrate them into your RAG system. This will ensure that the model consistently delivers high-quality results across different scenarios, improving the overall user experience and system performance.
Conclusion
Combining Relari and Qdrant allows you to create an iterative, data-driven evaluation framework, improving your RAG system for optimal real-world performance. These methods help ensure that your application is both responsive and effective, especially when dealing with user queries or recommendations.
If you’d like to get started, sign up for free at Qdrant Cloud and Relari.



































