Integrating Qdrant and LangChain for Advanced Vector Similarity Search
David Myriel
·March 12, 2024

On this page:
“Building AI applications doesn’t have to be complicated. You can leverage pre-trained models and support complex pipelines with a few lines of code. LangChain provides a unified interface, so that you can avoid writing boilerplate code and focus on the value you want to bring.” Kacper Lukawski, Developer Advocate, Qdrant
Long-Term Memory for Your GenAI App
Qdrant’s vector database quickly grew due to its ability to make Generative AI more effective. On its own, an LLM can be used to build a process-altering invention. With Qdrant, you can turn this invention into a production-level app that brings real business value.
The use of vector search in GenAI now has a name: Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). In our previous article, we argued why RAG is an essential component of AI setups, and why large-scale AI can’t operate without it. Numerous case studies explain that AI applications are simply too costly and resource-intensive to run using only LLMs.
Going forward, the solution is to leverage composite systems that use models and vector databases.
What is RAG? Essentially, a RAG setup turns Qdrant into long-term memory storage for LLMs. As a vector database, Qdrant manages the efficient storage and retrieval of user data.
Adding relevant context to LLMs can vastly improve user experience, leading to better retrieval accuracy, faster query speed and lower use of compute. Augmenting your AI application with vector search reduces hallucinations, a situation where AI models produce legitimate-sounding but made-up responses.
Qdrant streamlines this process of retrieval augmentation, making it faster, easier to scale and efficient. When you are accessing vast amounts of data (hundreds or thousands of documents), vector search helps your sort through relevant context. This makes RAG a primary candidate for enterprise-scale use cases.
Why LangChain?
Retrieval Augmented Generation is not without its challenges and limitations. One of the main setbacks for app developers is managing the entire setup. The integration of a retriever and a generator into a single model can lead to a raised level of complexity, thus increasing the computational resources required.
LangChain is a framework that makes developing RAG-based applications much easier. It unifies interfaces to different libraries, including major embedding providers like OpenAI or Cohere and vector stores like Qdrant. With LangChain, you can focus on creating tangible GenAI applications instead of writing your logic from the ground up.
Qdrant is one of the top supported vector stores on LangChain, with extensive documentation and examples.
How it Works: LangChain receives a query and retrieves the query vector from an embedding model. Then, it dispatches the vector to a vector database, retrieving relevant documents. Finally, both the query and the retrieved documents are sent to the large language model to generate an answer.
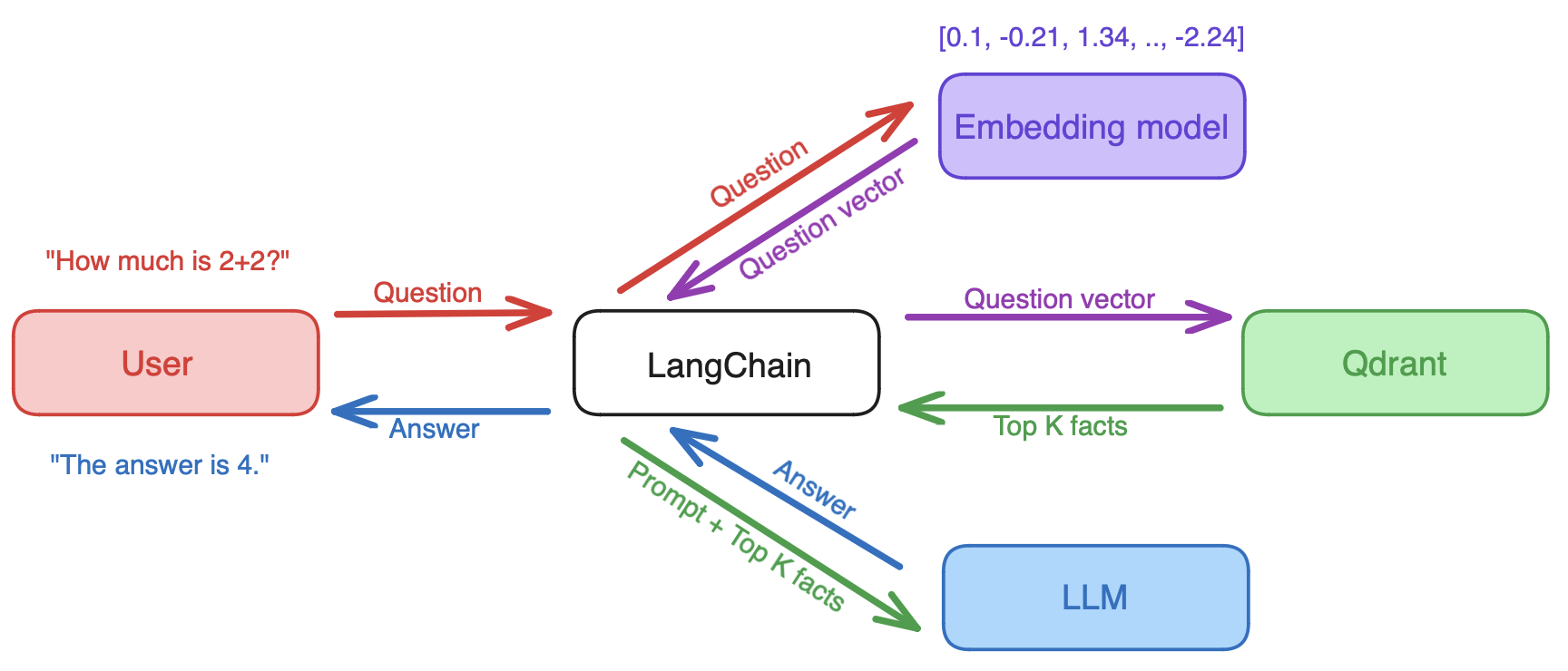
When supported by LangChain, Qdrant can help you set up effective question-answer systems, detection systems and chatbots that leverage RAG to its full potential. When it comes to long-term memory storage, developers can use LangChain to easily add relevant documents, chat history memory & rich user data to LLM app prompts via Qdrant.
Common Use Cases
Integrating Qdrant and LangChain can revolutionize your AI applications. Let’s take a look at what this integration can do for you:
Enhance Natural Language Processing (NLP): LangChain is great for developing question-answering chatbots, where Qdrant is used to contextualize and retrieve results for the LLM. We cover this in our article, and in OpenAI’s cookbook examples that use LangChain and GPT to process natural language.
Improve Recommendation Systems: Food delivery services thrive on indecisive customers. Businesses need to accomodate a multi-aim search process, where customers seek recommendations though semantic search. With LangChain you can build systems for e-commerce, content sharing, or even dating apps.
Advance Data Analysis and Insights: Sometimes you just want to browse results that are not necessarily closest, but still relevant. Semantic search helps user discover products in online stores. Customers don’t exactly know what they are looking for, but require constrained space in which a search is performed.
Offer Content Similarity Analysis: Ever been stuck seeing the same recommendations on your local news portal? You may be held in a similarity bubble! As inputs get more complex, diversity becomes scarce, and it becomes harder to force the system to show something different. LangChain developers can use semantic search to develop further context.
Building a Chatbot with LangChain
Now that you know how Qdrant and LangChain work together - it’s time to build something!
Follow Daniel Romero’s video and create a RAG Chatbot completely from scratch. You will only use OpenAI, Qdrant and LangChain. Here is what this basic tutorial will teach you:
1. How to set up a chatbot using Qdrant and LangChain: You will use LangChain to create a RAG pipeline that retrieves information from a dataset and generates output. This will demonstrate the difference between using an LLM by itself and leveraging a vector database like Qdrant for memory retrieval.
2. Preprocess and format data for use by the chatbot: First, you will download a sample dataset based on some academic journals. Then, you will process this data into embeddings and store it as vectors inside of Qdrant.
3. Implement vector similarity search algorithms: Second, you will create and test a chatbot that only uses the LLM. Then, you will enable the memory component offered by Qdrant. This will allow your chatbot to be modified and updated, giving it long-term memory.
4. Optimize the chatbot’s performance: In the last step, you will query the chatbot in two ways. First query will retrieve parametric data from the LLM, while the second one will get contexual data via Qdrant.
The goal of this exercise is to show that RAG is simple to implement via LangChain and yields much better results than using LLMs by itself.
Scaling Qdrant and LangChain
If you are looking to scale up and keep the same level of performance, Qdrant and LangChain are a rock-solid combination. Getting started with both is a breeze and the documentation covers a broad number of cases. However, the main strength of Qdrant is that it can consistently support the user way past the prototyping and launch phases.
“We are all-in on performance and reliability. Every release we make Qdrant faster, more stable and cost-effective for the user. When others focus on prototyping, we are already ready for production. Very soon, our users will build successful products and go to market. At this point, I anticipate a great need for a reliable vector store. Qdrant will be there for LangChain and the entire community.”
Whether you are building a bank fraud-detection system, RAG for e-commerce, or services for the federal government - you will need to leverage a scalable architecture for your product. Qdrant offers different features to help you considerably increase your application’s performance and lower your hosting costs.
Read more about out how we foster best practices for large-scale deployments.
Next Steps
Now that you know how Qdrant and LangChain can elevate your setup - it’s time to try us out.
Qdrant is open source and you can quickstart locally, install it via Docker, or to Kubernetes.
We also offer a free-tier of Qdrant Cloud for prototyping and testing.
For best integration with LangChain, read the official LangChain documentation.
For all other cases, Qdrant documentation is the best place to get there.
We offer additional support tailored to your business needs. Contact us to learn more about implementation strategies and integrations that suit your company.


































