Backing up Qdrant Cloud Clusters
Qdrant organizes cloud instances as clusters. On occasion, you may need to restore your cluster because of application or system failure.
You may already have a source of truth for your data in a regular database. If you have a problem, you could reindex the data into your Qdrant vector search cluster. However, this process can take time. For high availability critical projects we recommend replication. It guarantees the proper cluster functionality as long as at least one replica is running.
For other use-cases such as disaster recovery, you can set up automatic or self-service backups.
Prerequisites
You can back up your Qdrant clusters though the Qdrant Cloud Dashboard at https://cloud.qdrant.io. This section assumes that you’ve already set up your cluster, as described in the following sections:
- Create a cluster
- Set up Authentication
- Configure one or more Collections
Automatic Backups
You can set up automatic backups of your clusters with our Cloud UI. With the procedures listed in this page, you can set up snapshots on a daily/weekly/monthly basis. You can keep as many snapshots as you need. You can restore a cluster from the snapshot of your choice.
Note: When you restore a snapshot, consider the following:
- The affected cluster is not available while a snapshot is being restored.
- If you changed the cluster setup after the copy was created, the cluster resets to the previous configuration.
- The previous configuration includes:
- CPU
- Memory
- Node count
- Qdrant version
Configure a Backup
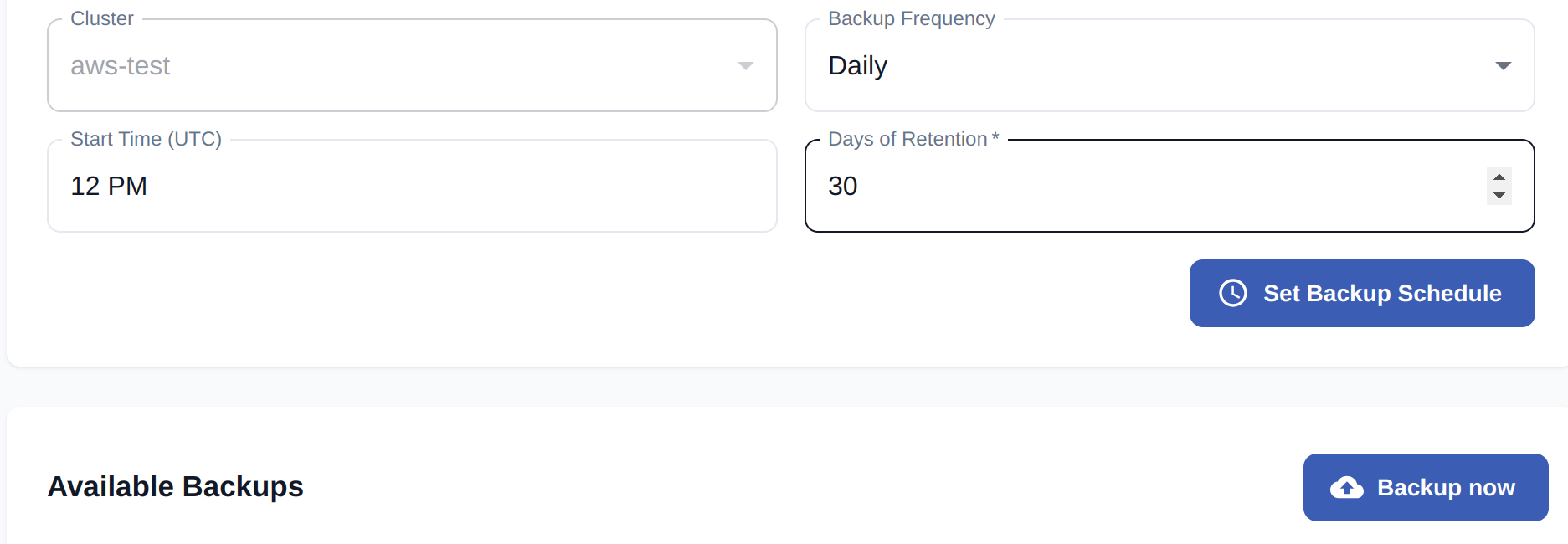
After you have taken the prerequisite steps, you can configure a backup with the Qdrant Cloud Dashboard. To do so, take these steps:
- On the Cluster Detail Page and select the Backups tab.
- Now you can set up a backup schedule. The Days of Retention is the number of days after a backup snapshot is deleted.
- Alternatively, you can select Backup now to take an immediate snapshot.
Restore a Backup
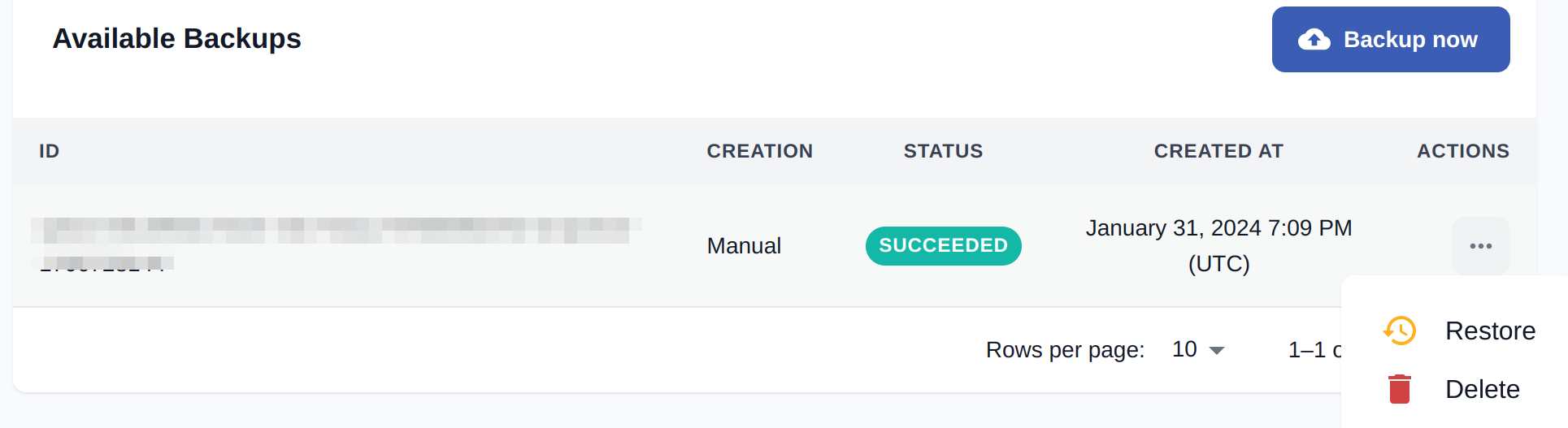
If you have a backup, it appears in the list of Available Backups. You can choose to restore or delete the backups of your choice.
Backups With a Snapshot
Qdrant also offers a snapshot API which allows you to create a snapshot of a specific collection or your entire cluster. For more information, see our snapshot documentation.
Here is how you can take a snapshot and recover a collection:
- Take a snapshot:
- For a single node cluster, call the snapshot endpoint on the exposed URL.
- For a multi node cluster call a snapshot on each node of the collection.
Specifically, prepend
node-{num}-to your cluster URL. Then call the snapshot endpoint on the individual hosts. Start with node 0. - In the response, you’ll see the name of the snapshot.
- Delete and recreate the collection.
- Recover the snapshot:
- Call the recover endpoint. Set a location which points to the snapshot file (
file:///qdrant/snapshots/{collection_name}/{snapshot_file_name}) for each host.
- Call the recover endpoint. Set a location which points to the snapshot file (
Backup Considerations
Backups are incremental for AWS and GCP clusters. For example, if you have two backups, backup number 2 contains only the data that changed since backup number 1. This reduces the total cost of your backups.
For Azure clusters, backups are based on total disk usage. The cost is calculated as half of the disk usage when the backup was taken.
You can create multiple backup schedules.
When you restore a snapshot, any changes made after the date of the snapshot are lost.


