
Agentic RAG Discord ChatBot with Qdrant, CAMEL-AI, & OpenAI
Unlike traditional RAG techniques, which passively retrieve context and generate responses, agentic RAG involves active decision-making and multi-step reasoning by the chatbot. Instead of just fetching data, the chatbot makes decisions, dynamically interacts with various data sources, and adapts based on context, giving it a much more dynamic and intelligent approach.
In this tutorial, we’ll develop a fully functional chatbot using Qdrant, CAMEL-AI, and OpenAI.
Let’s get started!
Workflow Overview
Below is a high-level look at our Agentic RAG workflow:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Environment Setup | Install required libraries (camel-ai, qdrant-client, discord.py) and set up the Python environment. |
| 2. Set Up the OpenAI Embedding Instance | Create an OpenAI account, generate an API key, and configure the embedding model. |
| 3. Configure the Qdrant Client | Sign up for Qdrant Cloud, create a cluster, configure QdrantStorage, and set up the API connection. |
| 4. Scrape and Process Data | Use VectorRetriever to scrape Qdrant documentation, chunk text, and store embeddings in Qdrant. |
| 5. Set Up the CAMEL-AI ChatAgent | Instantiate a CAMEL-AI ChatAgent with OpenAI models for multi-step reasoning and context-aware responses. |
| 6. Create and Configure the Discord Bot | Register a new bot in the Discord Developer Portal, invite it to a server, and enable permissions. |
| 7. Build the Discord Bot | Integrate Discord.py with CAMEL-AI and Qdrant to retrieve context and generate intelligent responses. |
| 8. Test the Bot | Run the bot in a live Discord server and verify that it provides relevant, context-rich answers. |
Architecture Diagram
Below is the architecture diagram representing the workflow and interactions of the chatbot:
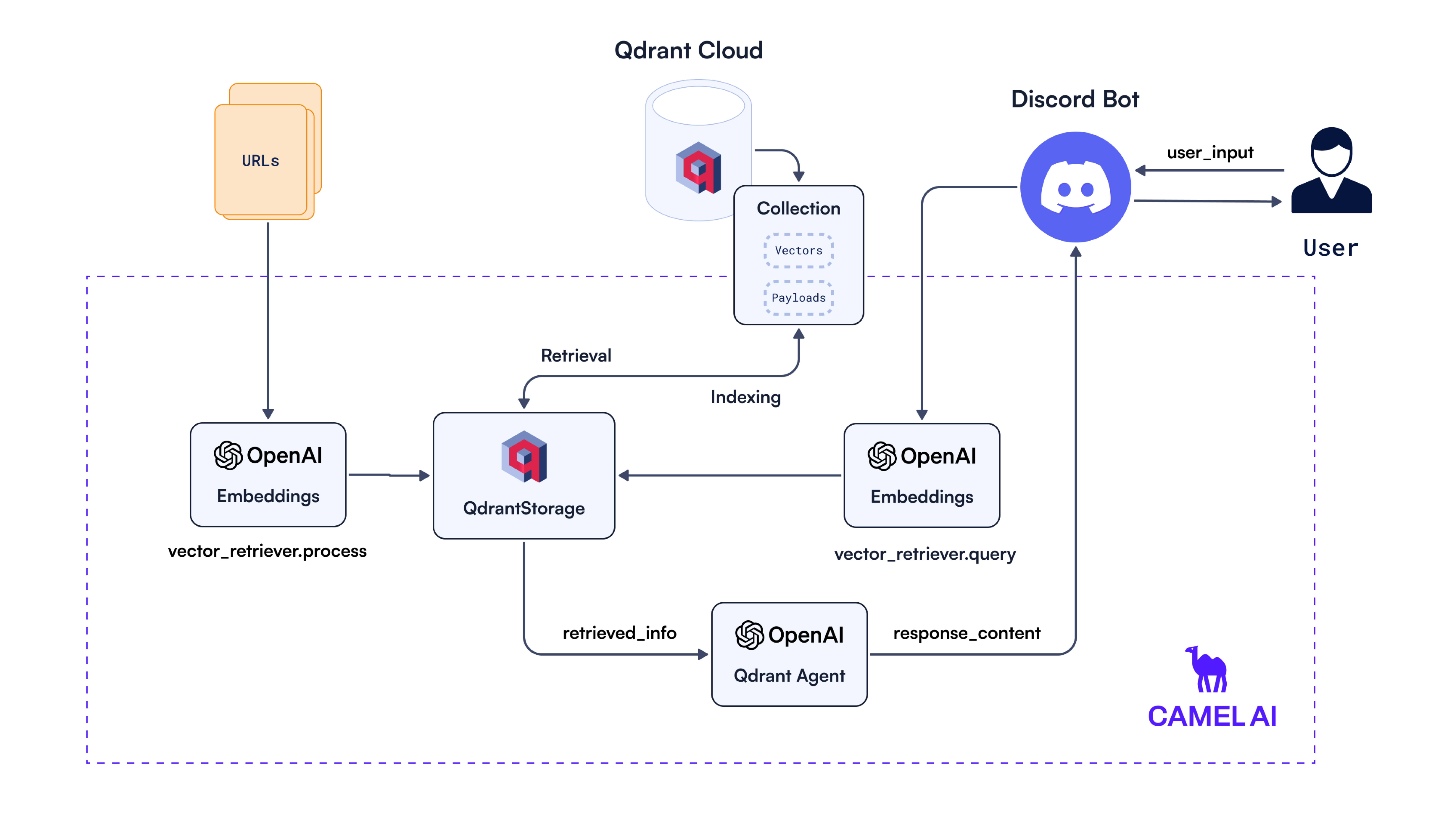
The workflow starts by scraping, chunking, and upserting content from URLs using the vector_retriever.process() method, which generates embeddings with the OpenAI embedding instance. These embeddings, along with their metadata, are then indexed and stored in Qdrant via the QdrantStorage class.
When a user sends a query through the Discord bot, it is processed by vector_retriever.query(), which first embeds the query using OpenAI Embeddings and then retrieves the most relevant matches from Qdrant via QdrantStorage. The retrieved context (e.g., relevant documentation snippets) is then passed to an OpenAI-powered Qdrant Agent under CAMEL-AI, which generates a final, context-aware response.
The Qdrant Agent processes the retrieved vectors using the GPT_4O_MINI language model, producing a response that is contextually relevant to the user’s query. This response is then sent back to the user through the Discord bot, completing the flow.
Step 1: Environment Setup
Before diving into the implementation, here’s a high-level overview of the stack we’ll use:
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Qdrant | Vector database for storing and querying document embeddings. |
| OpenAI | Embedding and language model for generating vector representations and chatbot responses. |
| CAMEL-AI | Framework for managing dialogue flow, retrieval, and AI agent interactions. |
| Discord API | Platform for deploying and interacting with the chatbot. |
Install Dependencies
We’ll install CAMEL-AI, which includes all necessary dependencies:
!pip install camel-ai[all]==0.2.17
Step 2: Set Up the OpenAI Embedding Instance
Create an OpenAI Account: Go to OpenAI and sign up for an account if you don’t already have one.
Generate an API Key:
After logging in, click on your profile icon in the top-right corner and select API keys.
Click Create new secret key.
Copy the generated API key and store it securely. You won’t be able to see it again.
Here’s how to set up the OpenAI client in your code:
Create a .env file in your project directory and add your API key:
OPENAI_API_KEY=<your_openai_api_key>
Make sure to replace <your_openai_api_key> with your actual API key.
Now, start the OpenAI Client
import openai
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
openai_client = openai.Client(
api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
)
To set up the embedding instance, we will use text embedding 3 large:
from camel.embeddings import OpenAIEmbedding
from camel.types import EmbeddingModelType
embedding_instance = OpenAIEmbedding(model_type=EmbeddingModelType.TEXT_EMBEDDING_3_LARGE)
Step 3: Configure the Qdrant Client
For this tutorial, we will be using the Qdrant Cloud Free Tier. Here’s how to set it up:
Create an Account: Sign up for a Qdrant Cloud account at Qdrant Cloud.
Create a Cluster:
- Navigate to the Overview section.
- Follow the onboarding instructions under Create First Cluster to set up your cluster.
- When you create the cluster, you will receive an API Key. Copy and securely store it, as you will need it later.
Wait for the Cluster to Provision:
- Your new cluster will appear under the Clusters section.
After obtaining your Qdrant Cloud details, add to your .env file:
QDRANT_CLOUD_URL=<your-qdrant-cloud-url>
QDRANT_CLOUD_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
Configure the QdrantStorage
The QdrantStorage will deal with connecting with the Qdrant Client for all necessary operations to your collection.
from camel.retrievers import VectorRetriever
# Define collection name
collection_name = "qdrant-agent"
storage_instance = QdrantStorage(
vector_dim=embedding_instance.get_output_dim(),
url_and_api_key=(
qdrant_cloud_url,
qdrant_api_key,
),
collection_name=collection_name,
)
Make sure to update the <your-qdrant-cloud-url> and <your-api-key> fields.
Step 4: Scrape and Process Data
We’ll use CamelAI VectorRetriever library to help us to It processes content from a file or URL, divides it into chunks, and stores the embeddings in the specified Qdrant collection.
from camel.retrievers import VectorRetriever
vector_retriever = VectorRetriever(embedding_model=embedding_instance,
storage=storage_instance)
qdrant_urls = [
"https://qdrant.tech/documentation/overview",
"https://qdrant.tech/documentation/guides/installation",
"https://qdrant.tech/documentation/concepts/filtering",
"https://qdrant.tech/documentation/concepts/indexing",
"https://qdrant.tech/documentation/guides/distributed_deployment",
"https://qdrant.tech/documentation/guides/quantization"
# Add more URLs as needed
]
for qdrant_url in qdrant_urls:
vector_retriever.process(
content=qdrant_url,
)
Step 5: Setup the CAMEL-AI ChatAgent Instance
Define the OpenAI model and create a CAMEL-AI ChatAgent instance.
from camel.configs import ChatGPTConfig
from camel.models import ModelFactory
from camel.types import ModelPlatformType, ModelType
from camel.agents import ChatAgent
# Create a ChatGPT configuration
config = ChatGPTConfig(temperature=0.2).as_dict()
# Create an OpenAI model using the configuration
openai_model = ModelFactory.create(
model_platform=ModelPlatformType.OPENAI,
model_type=ModelType.GPT_4O_MINI,
model_config_dict=config,
)
assistant_sys_msg = """You are a helpful assistant to answer question,
I will give you the Original Query and Retrieved Context,
answer the Original Query based on the Retrieved Context,
if you can't answer the question just say I don't know."""
qdrant_agent = ChatAgent(system_message=assistant_sys_msg, model=openai_model)
Step 6: Create and Configure the Discord Bot
Now let’s bring the bot to life! It will serve as the interface through which users can interact with the agentic RAG system you’ve built.
Create a New Discord Bot
Go to the Discord Developer Portal and log in with your Discord account.
Click on the New Application button.
Give your application a name and click Create.
Navigate to the Bot tab on the left sidebar and click Add Bot.
Once the bot is created, click Reset Token under the Token section to generate a new bot token. Copy this token securely as you will need it later.
Invite the Bot to Your Server
Go to the OAuth2 tab and then to the URL Generator section.
Under Scopes, select bot.
Under Bot Permissions, select the necessary permissions:
Send Messages
Read Message History
Copy the generated URL and paste it into your browser.
Select the server where you want to invite the bot and click Authorize.
Grant the Bot Permissions
Go back to the Bot tab.
Enable the following under Privileged Gateway Intents:
Server Members Intent
Message Content Intent
Now, the bot is ready to be integrated with your code.
Step 7: Build the Discord Bot
Add to your .env file:
DISCORD_BOT_TOKEN=<your-discord-bot-token>
We’ll use discord.py to create a simple Discord bot that interacts with users and retrieves context from Qdrant before responding.
from camel.bots import DiscordApp
import nest_asyncio
import discord
nest_asyncio.apply()
discord_q_bot = DiscordApp(token=os.getenv("DISCORD_BOT_TOKEN"))
@discord_q_bot.client.event # triggers when a message is sent in the channel
async def on_message(message: discord.Message):
if message.author == discord_q_bot.client.user:
return
if message.type != discord.MessageType.default:
return
if message.author.bot:
return
user_input = message.content
retrieved_info = vector_retriever.query(
query=user_input, top_k=10, similarity_threshold=0.6
)
user_msg = str(retrieved_info)
assistant_response = qdrant_agent.step(user_msg)
response_content = assistant_response.msgs[0].content
if len(response_content) > 2000: # discord message length limit
for chunk in [response_content[i:i+2000] for i in range(0, len(response_content), 2000)]:
await message.channel.send(chunk)
else:
await message.channel.send(response_content)
discord_q_bot.run()
Step 9: Test the Bot
Invite your bot to your Discord server using the OAuth2 URL from the Discord Developer Portal.
Run the notebook.
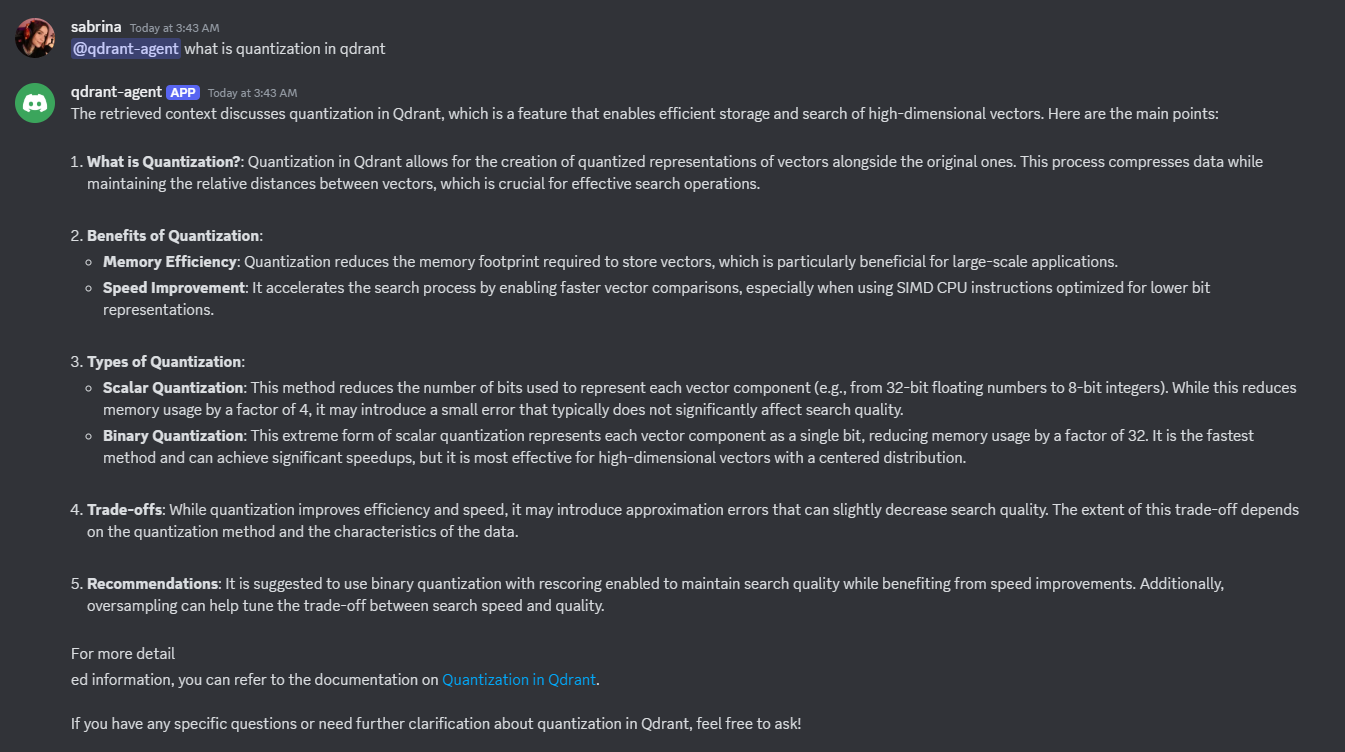
Start chatting with the bot in your Discord server. It will retrieve context from Qdrant and provide relevant answers based on your queries.
Conclusion
Nice work! You’ve built an agentic RAG-powered Discord bot that retrieves relevant information with Qdrant, generates smart responses with OpenAI, and handles multi-step reasoning using CAMEL-AI. Here’s a quick recap:
Smart Knowledge Retrieval: Your chatbot can now pull relevant info from large datasets using Qdrant’s vector search.
Autonomous Reasoning with CAMEL-AI: Enables multi-step reasoning instead of just regurgitating text.
Live Discord Deployment: You launched the chatbot on Discord, making it interactive and ready to help real users.
One of the biggest advantages of CAMEL-AI is the abstraction it provides, allowing you to focus on designing intelligent interactions rather than worrying about low-level implementation details.
You’re now well-equipped to tackle more complex real-world problems that require scalable, autonomous knowledge systems.


