Scaling Qdrant Cloud Clusters
The amount of data is always growing and at some point you might need to change the capacity of your cluster. You can easily scale your Qdrant cluster up or down from the Cluster detail page in the Qdrant Cloud console.
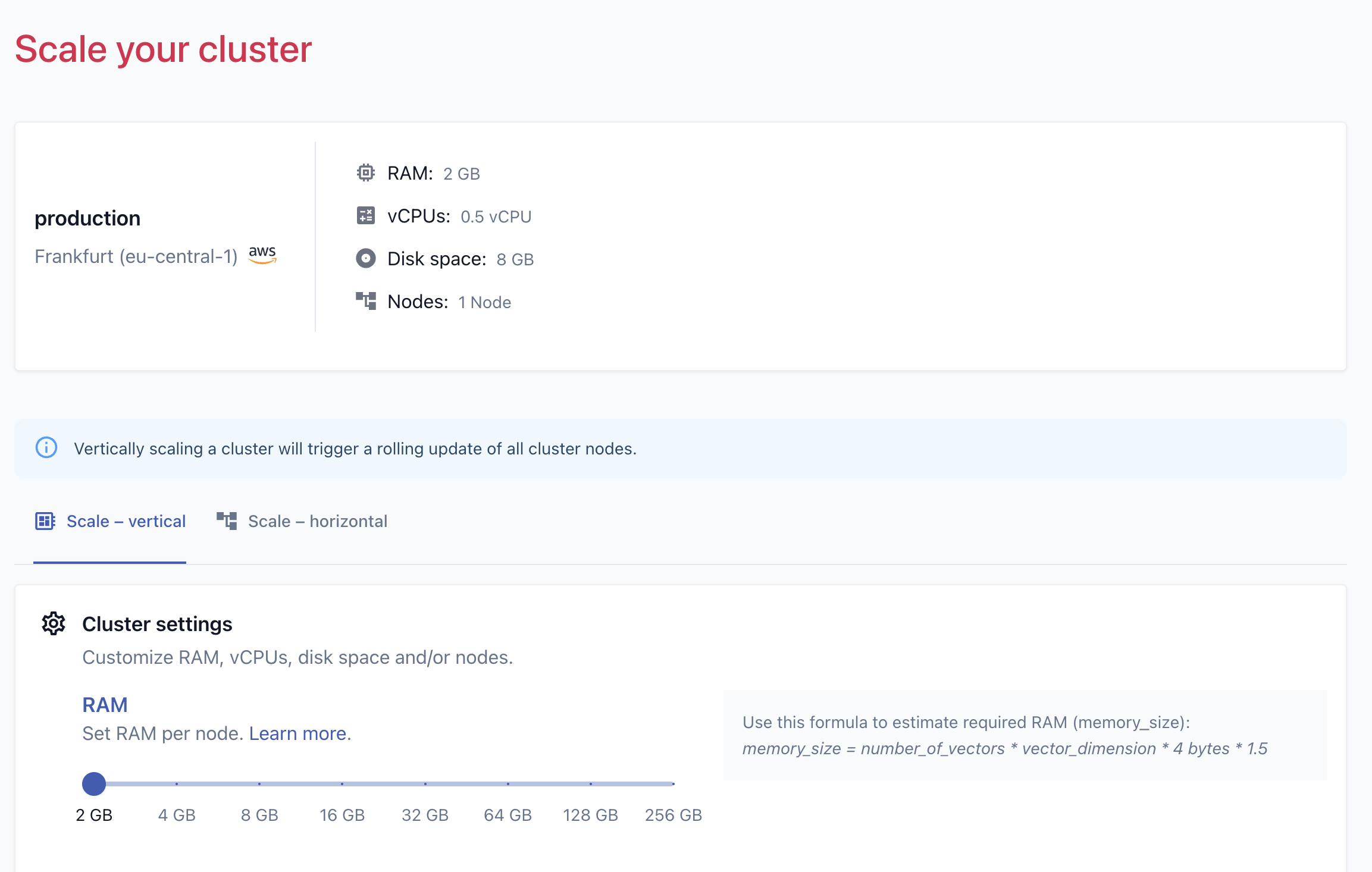
Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling is the process of increasing the capacity of a cluster by adding or removing CPU, storage and memory resources on each database node.
You can start with a minimal cluster configuration and scale it up over time to accomodate the growing amount of data in your application. If your cluster consists of several nodes each node will need to be scaled to the same size.
Note that vertical cluster scaling will require a short downtime, if the collections in your cluster are not replicated. This is because each node of the cluster needs to be restarted to apply the CPU, memory and disk size.
If you want to scale your cluster down, the new, smaller memory size must be still sufficient to store all the data in the cluster. Otherwise, the database cluster could run out of memory and crash. Therefore, the new memory size must be at least as large as the current memory usage of the database cluster including a bit of buffer. Qdrant Cloud will automatically prevent you from scaling down the Qdrant database cluster with a too small memory size.
Note, that it is not possible to scale down the disk space of the cluster due to technical limitations of the underlying cloud providers.
Horizontal Scaling
Vertical scaling can be an effective way to improve the performance of a cluster and extend the capacity, but it has some limitations. The main disadvantage of vertical scaling is that there are limits to how much a cluster can be expanded. At some point, adding more resources to a cluster can become impractical or cost-prohibitive.
In such cases, horizontal scaling may be a more effective solution.
Horizontal scaling is the process of increasing the capacity of a cluster by adding more nodes and distributing the load and data among them. The horizontal scaling at Qdrant starts on the collection level. You have to choose the number of shards you want to distribute your collection around while creating the collection. Please refer to the sharding documentation section for details.
When scaling up horizontally, the cloud platform will automatically rebalance all available shards across nodes to ensure that the data is evenly distributed. See Configuring Clusters for more details.
When scaling down horizontally, the cloud platform will automatically ensure that any shards that are present on the nodes to be deleted, are moved to the remaining nodes.
Important: One shard can not be split across nodes. So, if you configure 2 shards for a collection, but then scale your cluster from 1 to 3 nodes, your cluster nodes can’t be fully utilized. The cloud platform will automatically rebalance your shards, so that two nodes will have one shard each, but the third node will not have any shards at all. You can use the resharding feature to change the number of shards in an existing collection. Once resharding is complete, the cloud platform will rebalance the shards across all nodes, ensuring that all nodes are utilized.
We will be glad to consult you on an optimal strategy for scaling.
Let us know your needs and decide together on a proper solution.
Resharding
Available as of Qdrant v1.13.0
When creating a collection, it has a specific number of shards. The ideal number of shards might change as your cluster evolves.
Resharding allows you to change the number of shards in your existing collections, both up and down, without having to recreate the collection from scratch.
Resharding is a transparent process, meaning that the collection is still available while resharding is going on without having downtime. This allows you to scale from one node to any number of nodes and back, keeping your data perfectly distributed without compromise.
To increase the number of shards (reshard up), use the Update collection cluster setup API to initiate the resharding process:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/cluster
{
"start_resharding": {
"direction": "up",
"shard_key": null
}
}
To decrease the number of shards (reshard down), you may specify the "down" direction.
The current status of resharding is listed in the collection cluster info which can be fetched with:
GET /collections/{collection_name}/cluster
We always recommend to run an ongoing resharding operation till the end. But, if at any point the resharding operation needs to be aborted, you can use:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/cluster
{
"abort_resharding": {}
}
A few things to be aware of with regards to resharding:
- during resharding, performance of your cluster may be slightly reduced
- during resharding, reported point counts will not be accurate
- resharding may be a long running operation on huge collections
- you can only run one resharding operation per collection at a time


