Inference in Qdrant Managed Cloud
Inference is the process of creating vector embeddings from text, images, or other data types using a machine learning model.
Qdrant Managed Cloud allows you to use inference directly in the cloud, without the need to set up and maintain your own inference infrastructure. You can use embedding models hosted on Qdrant Cloud, or use externally hosted models.
Enabling/Disabling Inference
Inference is enabled by default for all new clusters, created after July, 7th 2025. You can enable it for existing clusters directly from the Inference tab of the Cluster Detail page in the Qdrant Cloud Console. Activating inference will trigger a restart of your cluster to apply the new configuration.
Using Inference
Inference can be easily used through the Qdrant SDKs and the REST or GRPC APIs when upserting points and when querying the database. Refer to the Inference documentation for details.
Cloud Inference
Clusters on Qdrant Managed Cloud can access embedding models that are hosted on Qdrant Cloud.
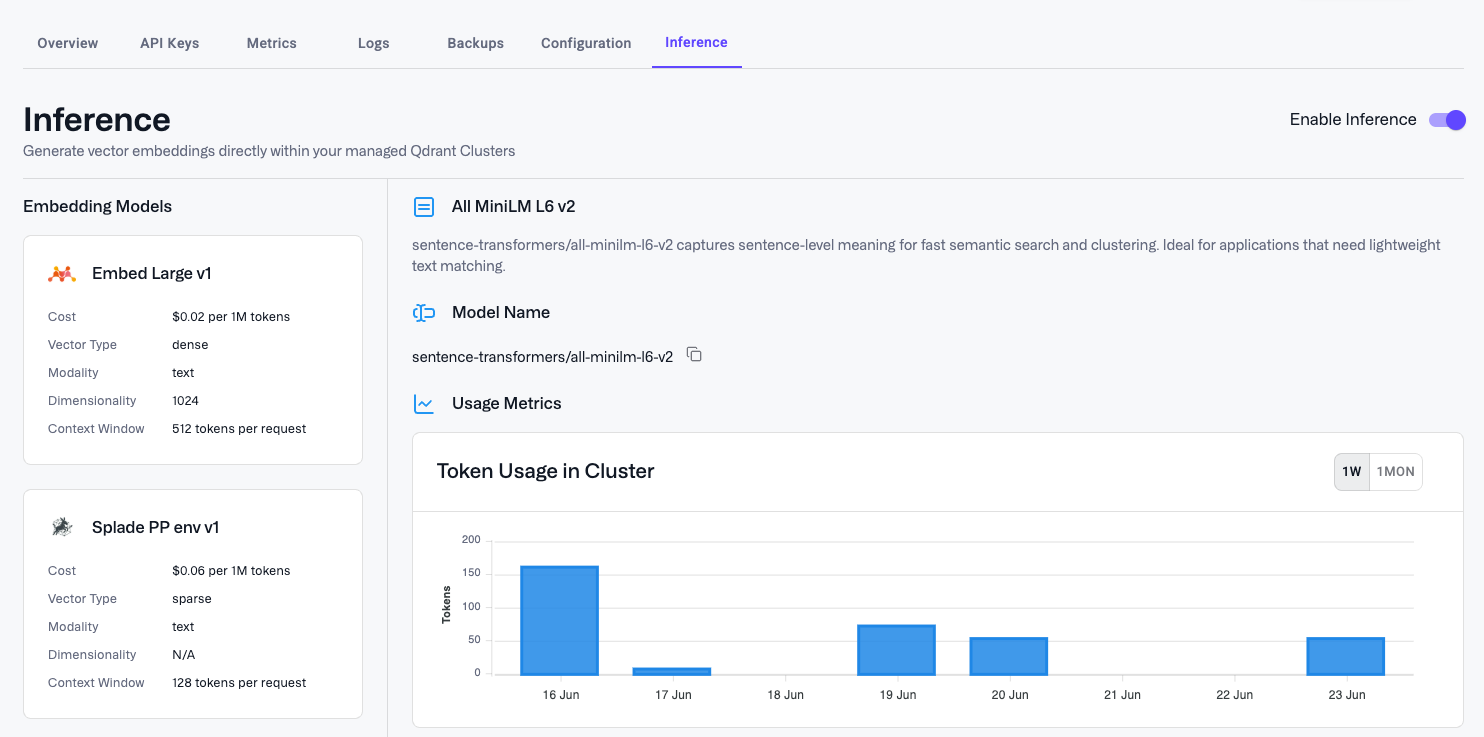
You can see the list of supported models in the Inference tab of the Cluster Detail page in the Qdrant Cloud Console. The list includes models for text, both to produce dense and sparse vectors, as well as multi-modal models for images.
Billing
Inference is billed based on the number of tokens processed by the model. The cost is calculated per 1,000,000 tokens. The price depends on the model and is displayed on the Inference tab of the Cluster Detail page. You also can see the current usage of each model there.
Use External Models
Qdrant Cloud can act as a proxy for the APIs of three external embedding model providers:
- OpenAI
- Cohere
- Jina AI
This enables you to access any of the embedding models provided by these providers through the Qdrant API.
Billing
To use an external provider’s embedding model, you need an API key from that provider. Billing is managed directly through the external provider, based on API key usage. Refer to each external embedding model provider’s website for pricing details.


